Page 61 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 61
Macro Economics
Notes 3. Capital Market: Producers raise investment to take advantage of new technology. This
raises income and in turn savings. Since both investment and saving rise, real ROI may
rise, fall or remain unchanged depending upon the relative increases in the two. Whatever
happens to the real ROI, the change in the real ROI brings in saving and investment
equality once again. Refer to the Figure 3.27. The investment curve shifts upwards and the
saving curve shifts rightwards. The new equilibrium is E and real ROI r . In this example,
2 2
r is greater than r . But r may also be less than or equal to r depending upon the relative
2 1 2 1
shifts of the I and S curves.
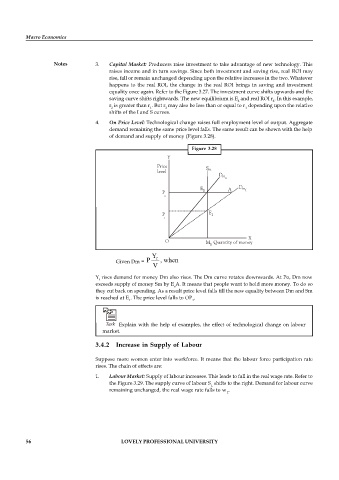
4. On Price Level: Technological change raises full employment level of output. Aggregate
demand remaining the same price level falls. The same result can be shown with the help
of demand and supply of money (Figure 3.28).
Figure 3.28
Y
Price
level S m
D m
o
E A D m
P 0 1
O
P E 1
1
X
O M 0 Quantity of money
Y
Given Dm = P f , when
V
Y rises demand for money Dm also rises. The Dm curve rotates downwards. At Po, Dm now
f
exceeds supply of money Sm by E A. It means that people want to hold more money. To do so
o
they cut back on spending. As a result price level falls till the new equality between Dm and Sm
is reached at E . The price level falls to OP .
1 1
Task Explain with the help of examples, the effect of technological change on labour
market.
3.4.2 Increase in Supply of Labour
Suppose more women enter into workforce. It means that the labour force participation rate
rises. The chain of effects are:
1. Labour Market: Supply of labour increases. This leads to fall in the real wage rate. Refer to
the Figure 3.29. The supply curve of labour S shifts to the right. Demand for labour curve
L
remaining unchanged, the real wage rate falls to w .
2
56 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY