Page 129 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 129
Quantitative Techniques-II
Notes
!
Caution The main disadvantage of this method of interviewing is that it takes time, and
the respondents may not co-operate.
Another disadvantage is that coding of open-ended questions may pose a challenge.
Example: When a researcher asks the respondent “Tell me something about your
experience in this hospital”. The answer may be “Well, the nurses are slow to attend and the
doctor is rude. ‘Slow’ and ‘rude’ are different qualities needing separate coding. This type of
interviewing is extremely helpful in exploratory studies.
Table 7.1: Types of Questionnaires
Types Characteristics
Structured – The same question is posed to each respondent.
Disguised Administering the questionnaire and post-administration work is simple i.e.
coding tabulating, etc. is easy.
This type of questionnaire is least used in market research.
Respondents’ bias is minimized.
Unstructured – This type of questionnaire is very commonly used for focus group
Disguised discussions.
This is difficult to analyse, code etc,
No fixed set of questions.
The inner self (why) of an individual is researched. Eg: Motivation Research.
Unstructured – No fixed questions.
Undisguised Suitable for conducting depth interview.
Subject-matter can be questioned in great detail.
Coding, tabulating etc. are difficult not a very frequently used method.
Structured – Fixed set of questions to every respondent.
Undisguised Inappropriate when researcher wants to probe deeper.
Easy to administer coding, tabulating is easy.
Due to structuring and undisguised nature of the questionnaire, there is no
possibility of the respondent misunderstanding the question. This is the most
commonly used method.
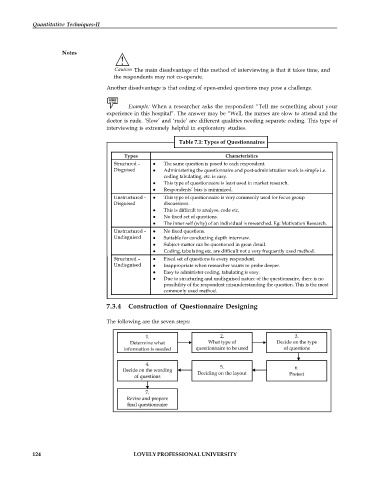
7.3.4 Construction of Questionnaire Designing
The following are the seven steps:
124 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY