Page 14 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 14
Unit 1: Quantitative Techniques for Managers
Situations in which each course of action (or strategy) can result in more than one pay-offs or Notes
consequences are called probabilistic models. Since in such models the concept of probability is
used, therefore the pay-off or consequences due to a managerial action cannot be predicted with
certainty.
Example: Simulation models, decision theory models etc.
Specified Behaviour Characteristics
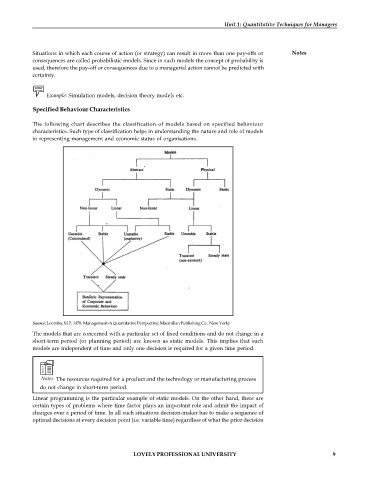
The following chart describes the classification of models based on specified behaviour
characteristics. Such type of classification helps in understanding the nature and role of models
in representing management and economic status of organisations.
Source: Loomba, M.P. 1978. Management-A Quantitative Perspective; Macmillan Publishing Co.: New York)
The models that are concerned with a particular set of fixed conditions and do not change in a
short-term period (or planning period) are known as static models. This implies that such
models are independent of time and only one decision is required for a given time period.
Notes The resources required for a product and the technology or manufacturing process
do not change in short-term period.
Linear programming is the particular example of static models. On the other hand, there are
certain types of problems where time factor plays an important role and admit the impact of
changes over a period of time. In all such situations decision-maker has to make a sequence of
optimal decisions at every decision point (i.e. variable time) regardless of what the prior decision
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9