Page 55 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 55
Quantitative Techniques-II
Notes then compute the calculated ‘Z’. This calculated value (absolute) is compared with tabulated
value obtained from normal distribution table against the decided criterion (value of ‘a’
and one tail or two tails).
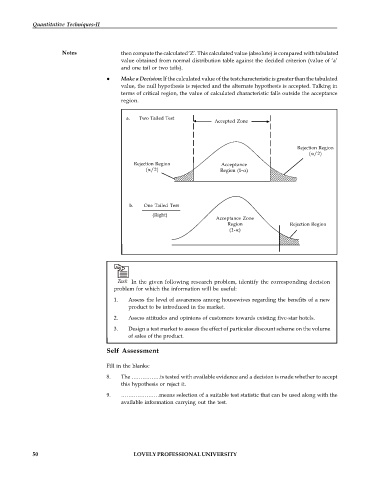
Make a Decision: If the calculated value of the test characteristic is greater than the tabulated
value, the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternate hypothesis is accepted. Talking in
terms of critical region, the value of calculated characteristic falls outside the acceptance
region.
a. Two Tailed Test
Accepted Zone
Rejection Region
(/2)
Rejection Region Acceptance
(/2) Region (1-)
b. One Tailed Test
(Right)
Acceptance Zone
Region Rejection Region
(1-)
Task In the given following research problem, identify the corresponding decision
problem for which the information will be useful:
1. Assess the level of awareness among housewives regarding the benefits of a new
product to be introduced in the market.
2. Assess attitudes and opinions of customers towards existing five-star hotels.
3. Design a test market to assess the effect of particular discount scheme on the volume
of sales of the product.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
8. The …………….is tested with available evidence and a decision is made whether to accept
this hypothesis or reject it.
9. …………………means selection of a suitable test statistic that can be used along with the
available information carrying out the test.
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY