Page 117 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 117
Management of Finances
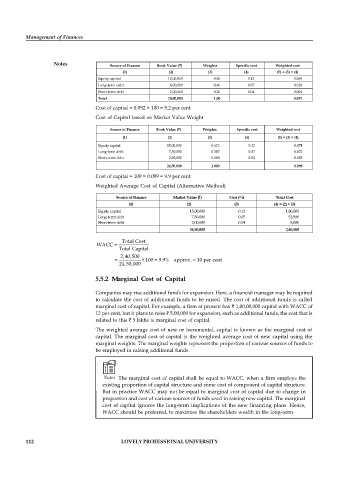
Notes Source of Finance Book Value ( ) Weights Specific cost Weighted cost
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) = (3) × (4)
Equity capital 10,00,000 0.50 0.12 0.060
Long-term debt 8,00,000 0.40 0.07 0.028
Short-term debt 2,00,000 0.10 0.04 0.004
Total 20,00,000 1.00 0.092
Cost of capital = 0.092 × 100 = 9.2 per cent
Cost of Capital based on Market Value Weight
Source of Finance Book Value ( ) Weights Specific cost Weighted cost
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) = (3) × (4)
Equity capital 15,00,000 0.613 0.12 0.074
Long-term debt 7,50,000 0.307 0.07 0.022
Short-term debt 2,00,000 0.080 0.04 0.003
24,50,000 1.000 0.099
Cost of capital = 100 × 0.099 = 9.9 per cent
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (Alternative Method)
Source of Finance Market Value ( ) Cost (%) Total Cost
(1) (2) (3) (4) = (2) × (3)
Equity capital 15,00,000 0.12 1,80,000
Long-term debt 7,50,000 0.07 52,500
Short-term debt 2,00,000 0.04 8,000
24,50,000 2,40,500
Total Cost
WACC =
Total Capital
2,40,500
= ×100 = 9.9% approx. 10 per cent
24,50,000
5.5.2 Marginal Cost of Capital
Companies may rise additional funds for expansion. Here, a financial manager may be required
to calculate the cost of additional funds to be raised. The cost of additional funds is called
marginal cost of capital. For example, a firm at present has 1,00,00,000 capital with WACC of
12 per cent, but it plans to raise 5,00,000 for expansion, such as additional funds, the cost that is
related to this 5 lakhs is marginal cost of capital.
The weighted average cost of new or incremental, capital is known as the marginal cost of
capital. The marginal cost of capital is the weighted average cost of new capital using the
marginal weights. The marginal weights represent the proportion of various sources of funds to
be employed in raising additional funds.
Notes The marginal cost of capital shall be equal to WACC, when a firm employs the
existing proportion of capital structure and some cost of component of capital structure.
But in practice WACC may not be equal to marginal cost of capital due to change in
proportion and cost of various sources of funds used in raising new capital. The marginal
cost of capital ignores the long-term implications of the new financing plans. Hence,
WACC should be preferred, to maximise the shareholders wealth in the long-term.
112 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY