Page 170 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 170
Unit 7: Concept of Leverages
8. The firms operating break-even point are the level of sale necessary to give all Notes
………………….. costs.
7.3 Financial Leverage
Financial leverage is defined as the ability of a firm to use fixed financial charges to magnify the
effects in EBIT/operating profits, on the firm’s earning per share, the two fixed financial cost that
may be found in the firms income statement are:
1. Interest on debt and
2. Dividends on preferred shares.
These charges must be paid regardless of the amount of EBIT available to pay them.
Notes The financial leverage is favourable when the firm earns more on the investments/
assets financed by the sources having fixed charges. It is obvious that shareholders gain in
a situation where a company earns a higher rate of return and pays a low rate to the
supplier of long term funds. Financial leverage in such cases is also called “trading in
equity.”
The degree of financial leverage is the nursical measure of the firms’ financial leverage and is
calculated as:
Financial leverage =
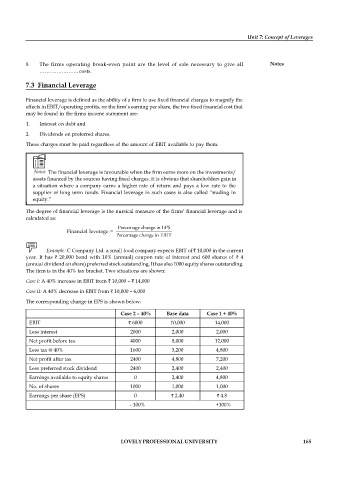
Example: C Company Ltd. a small food company expects EBIT of 10,000 in the current
year. It has 20,000 bond with 10% (annual) coupon rate of interest and 600 shares of 4
(annual dividend on share) preferred stock outstanding. It has also 1000 equity shares outstanding.
The firm is in the 40% tax bracket. Two situations are shown:
Case I: A 40% increase in EBIT from 10,000 – 14,000
Case II: A 40% decrease in EBIT from 10,000 – 6,000
The corresponding change in EPS is shown below:
Case 2 – 40% Base data Case 1 + 40%
EBIT 6000 10,000 14,000
Less interest 2000 2,000 2,000
Net profit before tax 4000 8,000 12,000
Less tax @ 40% 1600 3,200 4,800
Net profit after tax 2400 4,800 7,200
Less preferred stock dividend 2400 2,400 2,400
Earnings available to equity shares 0 2,400 4,800
No. of shares 1000 1,000 1,000
Earnings per share (EPS) 0 2.40 4.8
– 100% +100%
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 165