Page 195 - DMGT306_MERCANTILE_LAWS_II
P. 195
Mercantile Laws – II
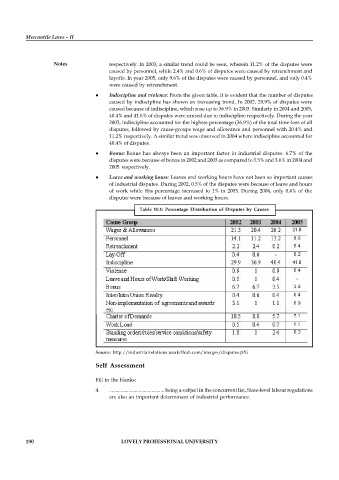
Notes respectively. In 2003, a similar trend could be seen, wherein 11.2% of the disputes were
caused by personnel, while 2.4% and 0.6% of disputes were caused by retrenchment and
layoffs. In year 2005, only 9.6% of the disputes were caused by personnel, and only 0.4%
were caused by retrenchment.
Indiscipline and violence: From the given table, it is evident that the number of disputes
caused by indiscipline has shown an increasing trend. In 2002, 29.9% of disputes were
caused because of indiscipline, which rose up to 36.9% in 2003. Similarly in 2004 and 2005,
40.4% and 41.6% of disputes were caused due to indiscipline respectively. During the year
2003, indiscipline accounted for the highest percentage (36.9%) of the total time-loss of all
disputes, followed by cause-groups wage and allowance and personnel with 20.4% and
11.2% respectively. A similar trend was observed in 2004 where indiscipline accounted for
40.4% of disputes.
Bonus: Bonus has always been an important factor in industrial disputes. 6.7% of the
disputes were because of bonus in 2002 and 2003 as compared to 3.5% and 3.6% in 2004 and
2005 respectively.
Leave and working hours: Leaves and working hours have not been so important causes
of industrial disputes. During 2002, 0.5% of the disputes were because of leave and hours
of work while this percentage increased to 1% in 2003. During 2004, only 0.4% of the
disputes were because of leaves and working hours.
Table 10.1: Percentage Distribution of Disputes by Causes
Source: http://industrialrelations.naukrihub.com/images/disputes.JPG
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
4. ........................................... being a subject in the concurrent list, State-level labour regulations
are also an important determinant of industrial performance.
190 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY