Page 117 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 117
Marketing Management/Essentials of Marketing
Notes 5.4 Positioning
Positioning is the perception of a brand or product it brings about in the mind of a target
consumer and reflects the essence of that brand or product in terms of its functional and non-
functional benefits as judged by the consumer.
Example: Nestle’s Maggi noodles has been successfully positioned as the “two minute”
noodle in the minds of target consumers and has created a distinctive brand image. HUL’s soap
Lux is the “beauty soap” of female film stars and Dettol is the antiseptic for minor nicks and cuts.
BMW car is positioned as the “ultimate driving machine”.
As markets become more crowded and competitive with similar types of products, consumers
rely more on the product’s image than on its actual characteristics in making their buying
decisions.
5.4.1 Positioning Maps
Products or services are ‘mapped’ together on a ‘positioning map’. This allows them to be
compared and contrasted in relation to each other. This is the main strength of this tool. Marketers
decide upon a competitive position which enables them to distinguish their own products from
the offerings of their competition (hence the term positioning strategy).
!
Caution The marketer would draw out the map and decide upon a label for each axis. They
could be price (variable one) and quality (variable two), or Comfort (variable one) and
price (variable two). The individual products are then mapped out next to each other Any
gaps could be regarded as possible areas for new products.
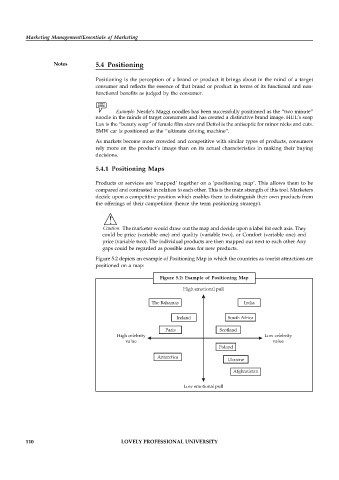
Figure 5.2 depicts an example of Positioning Map in which the countries as tourist attractions are
positioned on a map:
Figure 5.2: Example of Positioning Map
High emotional pull
The Bahamas India
Ireland South Africa
Paris Scotland
High celebrity Low celebrity
value value
Poland
Antarctica
Ukraine
Afghanistan
Low emotional pull
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY