Page 144 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 144
Unit 6: Products, Services and Brands
Notes
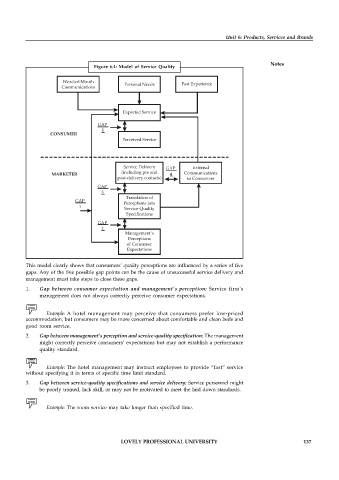
Figure 6.4: Model of Service Quality
Word-of-Mouth Past Experience
Communications Personal Needs
Expected Service
GAP
5
CONSUMER
Perceived Service
Service Delivery GAP External
MARKETER (including pre and 4 Communications
post-delivery contacts) to Consumers
GAP
3
Translation of
GAP Perceptions into
1
Service-Quality
Specifications
GAP
2
Management’s
Perceptions
of Consumer
Expectations
This model clearly shows that consumers’ quality perceptions are influenced by a series of five
gaps. Any of the five possible gap points can be the cause of unsuccessful service delivery and
management must take steps to close these gaps.
1. Gap between consumer expectation and management’s perception: Service firm’s
management does not always correctly perceive consumer expectations.
Example: A hotel management may perceive that consumers prefer low-priced
accommodation, but consumers may be more concerned about comfortable and clean beds and
good room service.
2. Gap between management’s perception and service-quality specification: The management
might correctly perceive consumers’ expectations but may not establish a performance
quality standard.
Example: The hotel management may instruct employees to provide “fast” service
without specifying it in terms of specific time limit standard.
3. Gap between service-quality specifications and service delivery: Service personnel might
be poorly trained, lack skill, or may not be motivated to meet the laid down standards.
Example: The room service may take longer than specified time.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 137