Page 173 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 173
Marketing Management/Essentials of Marketing
Notes
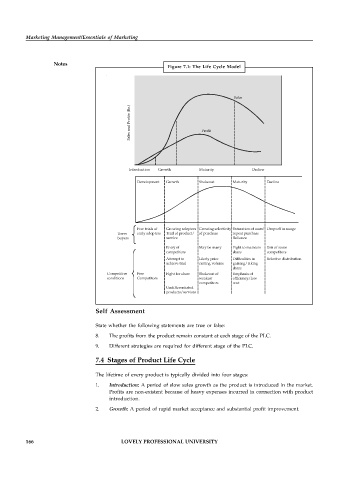
Figure 7.1: The Life Cycle Model
Sales
Sales and Profits (Rs.) Profit
Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
Development Growth Shakeout Maturity Decline
Few trials of Growing adopters Growing selectivity Saturation of users' Drop-off in usage
Users early adopters Trail of product/ of purchase repeat purchase
buyers service Reliance
Entry of May be many Fight to maintain Exit of some
competitors share competitors
Attempt to Likely price Difficulties in Selective distribution
achieve trial cutting volume gaining/taking
share
Competitive Few Fight for share Shakeout of Emphasis of
conditions Competitors weakest efficiency/low
competitors cost
Undifferentiated
products/services
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are true or false:
8. The profits from the product remain constant at each stage of the PLC.
9. Different strategies are required for different stage of the PLC.
7.4 Stages of Product Life Cycle
The lifetime of every product is typically divided into four stages:
1. Introduction: A period of slow sales growth as the product is introduced in the market.
Profits are non-existent because of heavy expenses incurred in connection with product
introduction.
2. Growth: A period of rapid market acceptance and substantial profit improvement.
166 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY