Page 62 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 62
Unit 2: Understanding the Marketplace and Consumers
Notes
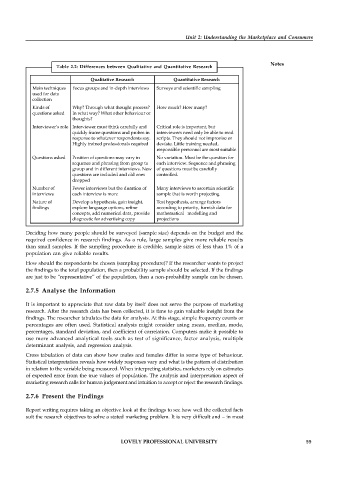
Table 2.2: Differences between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative Research Quantitative Research
Main techniques Focus groups and in-depth interviews Surveys and scientific sampling
used for data
collection
Kinds of Why? Through what thought process? How much? How many?
questions asked In what way? What other behaviour or
thoughts?
Interviewer’s role Interviewer must think carefully and Critical role is important, but
quickly frame questions and probes in interviewers need only be able to read
response to whatever respondents say. scripts. They should not improvise or
Highly trained professionals required deviate. Little training needed,
responsible personnel are most suitable
Questions asked Position of questions may vary in No variation. Must be the question for
sequence and phrasing from group to each interview. Sequence and phrasing
group and in different interviews. New of questions must be carefully
questions are included and old ones controlled.
dropped
Number of Fewer interviews but the duration of Many interviews to ascertain scientific
interviews each interview is more sample that is worth projecting
Nature of Develop a hypothesis, gain insight, Test hypothesis, arrange factors
findings explore language options, refine according to priority, furnish data for
concepts, add numerical data, provide mathematical modelling and
diagnostic for advertising copy projections
Deciding how many people should be surveyed (sample size) depends on the budget and the
required confidence in research findings. As a rule, large samples give more reliable results
than small samples. If the sampling procedure is credible, sample sizes of less than 1% of a
population can give reliable results.
How should the respondents be chosen (sampling procedure)? If the researcher wants to project
the findings to the total population, then a probability sample should be selected. If the findings
are just to be “representative” of the population, then a non-probability sample can be chosen.
2.7.5 Analyse the Information
It is important to appreciate that raw data by itself does not serve the purpose of marketing
research. After the research data has been collected, it is time to gain valuable insight from the
findings. The researcher tabulates the data for analysis. At this stage, simple frequency counts or
percentages are often used. Statistical analysis might consider using mean, median, mode,
percentages, standard deviation, and coefficient of correlation. Computers make it possible to
use more advanced analytical tools such as test of significance, factor analysis, multiple
determinant analysis, and regression analysis.
Cross tabulation of data can show how males and females differ in some type of behaviour.
Statistical interpretation reveals how widely responses vary and what is the pattern of distribution
in relation to the variable being measured. When interpreting statistics, marketers rely on estimates
of expected error from the true values of population. The analysis and interpretation aspect of
marketing research calls for human judgement and intuition to accept or reject the research findings.
2.7.6 Present the Findings
Report writing requires taking an objective look at the findings to see how well the collected facts
suit the research objectives to solve a stated marketing problem. It is very difficult and – in most
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 55