Page 109 - DCOM506_DMGT502_STRATEGIC_MANAGEMENT
P. 109
Unit 6: Organisational Appraisal: Internal Assessment 2
above, resources can be typically grouped under four headings: Physical resources, human Notes
resources, financial resources and intellectual capital.
Threshold Resources
A set of basic resources are needed by a firm for its existence and survival in the marketplace.
These resources are called ‘threshold resources’. But this threshold tends to increase with time.
So, a firm needs to continuously improve this threshold resource base just to stay in business.
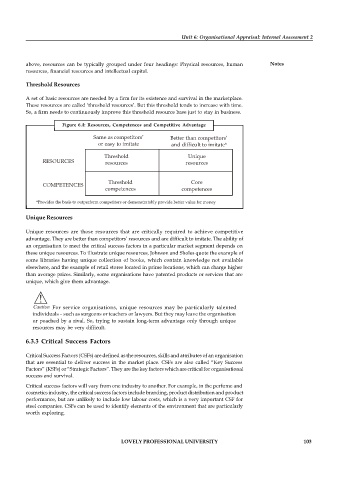
Figure 6.4: Resources, Competences and Competitive Advantage
Same as competitors’ Better than competitors’
or easy to imitate and difficult to imitate*
Threshold Unique
RESOURCES resources resources
Threshold Core
COMPETENCES
competences competences
*Provides the basis to outperform competitors or demonstratably provide better value for money
Unique Resources
Unique resources are those resources that are critically required to achieve competitive
advantage. They are better than competitors’ resources and are difficult to imitate. The ability of
an organisation to meet the critical success factors in a particular market segment depends on
these unique resources. To illustrate unique resources, Johnson and Sholes quote the example of
some libraries having unique collection of books, which contain knowledge not available
elsewhere, and the example of retail stores located in prime locations, which can charge higher
than average prices. Similarly, some organisations have patented products or services that are
unique, which give them advantage.
!
Caution For service organisations, unique resources may be particularly talented
individuals – such as surgeons or teachers or lawyers. But they may leave the organisation
or poached by a rival. So, trying to sustain long-term advantage only through unique
resources may be very difficult.
6.3.3 Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSFs) are defined as the resources, skills and attributes of an organisation
that are essential to deliver success in the market place. CSFs are also called “Key Success
Factors” (KSFs) or “Strategic Factors”. They are the key factors which are critical for organisational
success and survival.
Critical success factors will vary from one industry to another. For example, in the perfume and
cosmetics industry, the critical success factors include branding, product distribution and product
performance, but are unlikely to include low labour costs, which is a very important CSF for
steel companies. CSFs can be used to identify elements of the environment that are particularly
worth exploring.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 103