Page 303 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 303
Unit 13: Supply Chain Management and JIT
Notes
2. Reduce greenhouse gases by 20 percent in 7 years
3. Reduce energy use at stores by 30 percent in 7 years
4. Cut solid waste from U.S. stores and Sam’s Clubs by 25 percent in three years.
5. Buying diesel-electric and refrigerated trucks with a power unit that could keep
cargo cold without the engine running, saving nearly $75 million in fuel costs and
eliminating an estimated 400,000 tons of CO pollution in one year alone
2
6. Making a five-year verbal commitment to buy only organically grown cotton from
farmers, and to buy alternate crops those farmers need to grow between cotton
harvests. Last year, the company became the world's largest buyer of organic cotton
7. Promising by 2011 to only carry seafood certified wild by the Marine Stewardship
Council, a group dedicated to preventing the depletion of ocean life from overfishing.
8. Buying (and selling) 12 weeks' worth of Restrictions on Hazardous Substances
(RoHS)- compliant computers from Toshiba.
Although this may seem like a very large list for a company to accomplish, each of these
are attainable and place Wal-Mart in a great competitive position for the future.
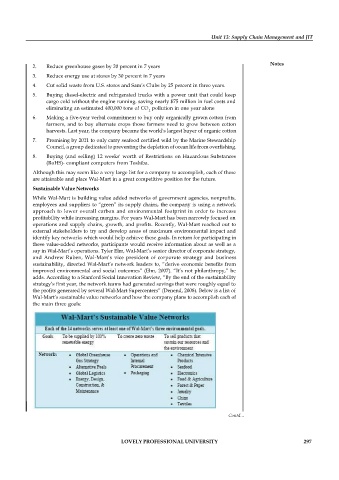
Sustainable Value Networks
While Wal-Mart is building value added networks of government agencies, nonprofits,
employees and suppliers to “green” its supply chains, the company is using a network
approach to lower overall carbon and environmental footprint in order to increase
profitability while increasing margins. For years Wal-Mart has been narrowly focused on
operations and supply chains, growth, and profits. Recently, Wal-Mart reached out to
external stakeholders to try and develop areas of maximum environmental impact and
identify key networks which would help achieve these goals. In return for participating in
these value-added networks, participants would receive information about as well as a
say in Wal-Mart’s operations. Tyler Elm, Wal-Mart’s senior director of corporate strategy,
and Andrew Ruben, Wal-Mart’s vice president of corporate strategy and business
sustainability, directed Wal-Mart’s network leaders to, “derive economic benefits from
improved environmental and social outcomes” (Elm, 2007). “It’s not philanthropy,” he
adds. According to a Stanford Social Innovation Review, “By the end of the sustainability
strategy’s first year, the network teams had generated savings that were roughly equal to
the profits generated by several Wal-Mart Supercenters” (Denend, 2008). Below is a list of
Wal-Mart’s sustainable value networks and how the company plans to accomplish each of
the main three goals:
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 297