Page 13 - DMGT522_SERVICES MANAGEMENT
P. 13
Services Management
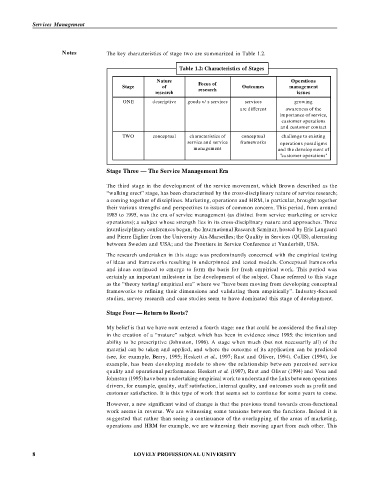
Notes The key characteristics of stage two are summarized in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2: Characteristics of Stages
Nature Operations
Stage of Focus of Outcomes management
research
research issues
ONE descriptive goods v/s services services growing
are different awareness of the
importance of service,
customer operations
and customer contact
TWO conceptual characteristics of conceptual challenge to existing
service and service frameworks operations paradigms
management and the development of
"customer operations"
Stage Three — The Service Management Era
The third stage in the development of the service movement, which Brown described as the
“walking erect” stage, has been characterised by the cross-disciplinary nature of service research;
a coming together of disciplines. Marketing, operations and HRM, in particular, brought together
their various strengths and perspectives to issues of common concern. This period, from around
1985 to 1995, was the era of service management (as distinct from service marketing or service
operations); a subject whose strength lies in its cross-disciplinary nature and approaches. Three
interdisciplinary conferences began, the International Research Seminar, hosted by Eric Langeard
and Pierre Eiglier from the University Aix-Marseilles; the Quality in Services (QUIS), alternating
between Sweden and USA; and the Frontiers in Service Conference at Vanderbilt, USA.
The research undertaken in this stage was predominantly concerned with the empirical testing
of ideas and frameworks resulting in underpinned and tested models. Conceptual frameworks
and ideas continued to emerge to form the basis for fresh empirical work. This period was
certainly an important milestone in the development of the subject. Chase referred to this stage
as the “theory testing/empirical era” where we “have been moving from developing conceptual
frameworks to refining their dimensions and validating them empirically”. Industry-focused
studies, survey research and case studies seem to have dominated this stage of development.
Stage Four — Return to Roots?
My belief is that we have now entered a fourth stage: one that could be considered the final step
in the creation of a “mature” subject which has been in evidence since 1995: the intention and
ability to be prescriptive (Johnston, 1996). A stage when much (but not necessarily all) of the
material can be taken and applied, and where the outcome of its application can be predicted
(see, for example, Berry, 1995; Heskett et al., 1997; Rust and Oliver, 1994). Collier (1994), for
example, has been developing models to show the relationship between perceived service
quality and operational performance. Heskett et al. (1997), Rust and Oliver (1994) and Voss and
Johnston (1995) have been undertaking empirical work to understand the links between operations
drivers, for example, quality, staff satisfaction, internal quality, and outcomes such as profit and
customer satisfaction. It is this type of work that seems set to continue for some years to come.
However, a new significant wind of change is that the previous trend towards cross-functional
work seems in reverse. We are witnessing some tensions between the functions. Indeed it is
suggested that rather than seeing a continuance of the overlapping of the areas of marketing,
operations and HRM for example, we are witnessing their moving apart from each other. This
8 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY