Page 296 - DMGT545_INTERNATIONAL_BUSINESS
P. 296
Unit 15: Global Strategic Management and Business Ethics
A transnational strategy makes sense when a firm faces high pressures for cost reductions, high notes
pressures for local responsiveness, and where there are significant opportunities for leveraging
valuable skills within a multinational’s global network of operations. In some ways, firms
that pursue a transnational strategy are trying to simultaneously achieve cost and differential
advantages. In terms of framework they are trying to simultaneously lower C and increase V.
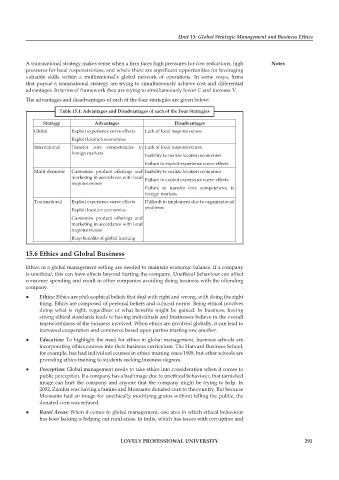
The advantages and disadvantages of each of the four strategies are given below:
table 15.1: advantages and Disadvantages of each of the four strategies
strategy advantages Disadvantages
Global Exploit experience curve effects Lack of local responsiveness
Exploit location economies
International Transfer core competencies to Lack of local responsiveness.
foreign markets Inability to realize location economies
Failure to exploit experience curve effects
Multi-domestic Customize product offerings and Inability to realize location economies
marketing in accordance with local Failure to exploit experience curve effects
responsiveness
Failure to transfer core competencies to
foreign markets
Transnational Exploit experience curve effects Difficult to implement due to organizational
Exploit location economies problems
Customize product offerings and
marketing in accordance with local
responsiveness
Reap benefits of global learning
15.6 ethics and Global Business
Ethics in a global management setting are needed to maintain economic balance. If a company
is unethical, this can have effects beyond hurting the company. Unethical behaviour can affect
consumer spending and result in other companies avoiding doing business with the offending
company.
l z Ethics: Ethics are philosophical beliefs that deal with right and wrong, with doing the right
thing. Ethics are composed of personal beliefs and cultural norms. Being ethical involves
doing what is right, regardless of what benefits might be gained. In business, having
strong ethical standards leads to having individuals and businesses believe in the overall
trustworthiness of the business involved. When ethics are involved globally, it can lead to
increased cooperation and commerce based upon parties trusting one another.
l z Education: To highlight the need for ethics in global management, business schools are
incorporating ethics courses into their business curriculum. The Harvard Business School,
for example, has had individual courses in ethics training since 1908, but other schools are
providing ethics training to students seeking business degrees.
l z Perception: Global management needs to take ethics into consideration when it comes to
public perception. If a company has a bad image due to unethical behaviour, that tarnished
image can hurt the company and anyone that the company might be trying to help. In
2002, Zambia was having a famine and Monsanto donated corn to the country. But because
Monsanto had an image for unethically modifying grains without telling the public, the
donated corn was refused.
l z Rural Areas: When it comes to global management, one area in which ethical behaviour
has been lacking is helping out rural areas. In India, which has issues with corruption and
lovely Professional university 291