Page 116 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 116
Software Project Management
Notes
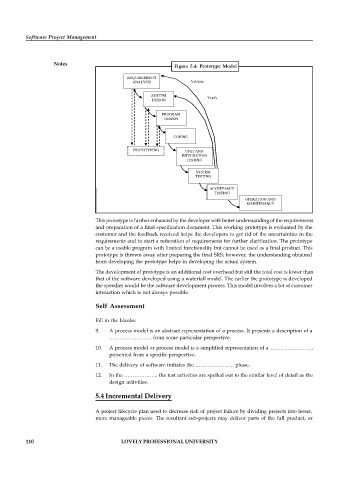
Figure 5.4: Prototype Model
REQUIREMENTS
ANALYSIS Validate
SYSTEM
Verify
DESIGN
PROGRAM
DESIGN
CODING
PROTOTYPING UNIT AND
INTEGRATION
TESTING
SYSTEM
TESTING
ACCEPTANCE
TESTING
OPERATION AND
MAINTENANCE
This prototype is further enhanced by the developer with better understanding of the requirements
and preparation of a final specification document. This working prototype is evaluated by the
customer and the feedback received helps the developers to get rid of the uncertainties in the
requirements and to start a reiteration of requirements for further clarification. The prototype
can be a usable program with limited functionality but cannot be used as a final product. This
prototype is thrown away after preparing the final SRS; however, the understanding obtained
from developing the prototype helps in developing the actual system.
The development of prototype is an additional cost overhead but still the total cost is lower than
that of the software developed using a waterfall model. The earlier the prototype is developed
the speedier would be the software development process. This model involves a lot of customer
interaction which is not always possible.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
9. A process model is an abstract representation of a process. It presents a description of a
……………………. from some particular perspective.
10. A process model or process model is a simplified representation of a ……………………,
presented from a specific perspective.
11. The delivery of software initiates the ………………….. phase.
12. In the ……………….. the test activities are spelled out to the similar level of detail as the
design activities.
5.4 Incremental Delivery
A project lifecycle plan used to decrease risk of project failure by dividing projects into lesser,
more manageable pieces. The resultant sub-projects may deliver parts of the full product, or
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY