Page 210 - DCAP309_INFORMATION_SECURITY_AND_PRIVACY
P. 210
Information Security and Privacy
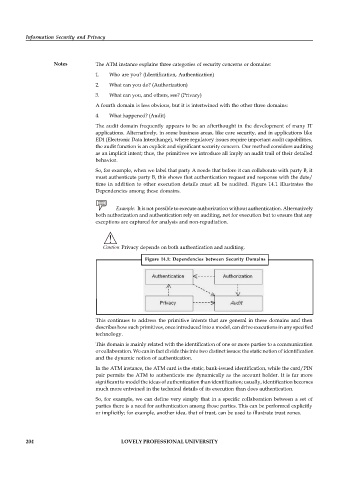
Notes The ATM instance explains three categories of security concerns or domains:
1. Who are you? (Identification, Authentication)
2. What can you do? (Authorization)
3. What can you, and others, see? (Privacy)
A fourth domain is less obvious, but it is intertwined with the other three domains:
4. What happened? (Audit)
The audit domain frequently appears to be an afterthought in the development of many IT
applications. Alternatively, in some business areas, like core security, and in applications like
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), where regulatory issues require important audit capabilities,
the audit function is an explicit and significant security concern. Our method considers auditing
as an implicit intent; thus, the primitives we introduce all imply an audit trail of their detailed
behavior.
So, for example, when we label that party A needs that before it can collaborate with party B, it
must authenticate party B, this shows that authentication request and response with the date/
time in addition to other execution details must all be audited. Figure 14.1 Illustrates the
Dependencies among these domains.
Example: It is not possible to execute authorization without authentication. Alternatively
both authorization and authentication rely on auditing, not for execution but to ensure that any
exceptions are captured for analysis and non-repudiation.
!
Caution Privacy depends on both authentication and auditing.
Figure 14.1: Dependencies between Security Domains
This continues to address the primitive intents that are general in these domains and then
describes how such primitives, once introduced into a model, can drive executions in any specified
technology.
This domain is mainly related with the identification of one or more parties to a communication
or collaboration. We can in fact divide this into two distinct issues: the static notion of identification
and the dynamic notion of authentication.
In the ATM instance, the ATM card is the static, bank-issued identification, while the card/PIN
pair permits the ATM to authenticate me dynamically as the account holder. It is far more
significant to model the ideas of authentication than identification; usually, identification becomes
much more entwined in the technical details of its execution than does authentication.
So, for example, we can define very simply that in a specific collaboration between a set of
parties there is a need for authentication among those parties. This can be performed explicitly
or implicitly; for example, another idea, that of trust, can be used to illustrate trust zones.
204 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY