Page 158 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 158
Unit 8: Databases and Data Warehouses
Notes
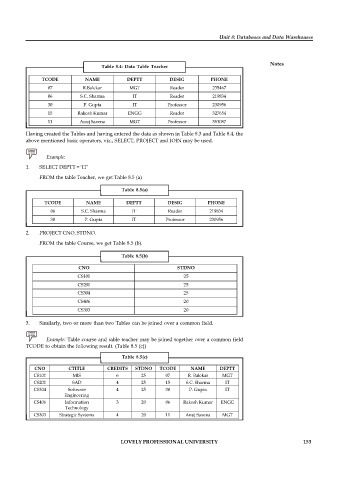
Table 8.4: Data Table Teacher
TCODE NAME DEPTT DESIG PHONE
07 R.Balekar MGT Reader 235467
06 S.C. Sharma IT Reader 219834
30 P. Gupta IT Professor 230956
15 Rakesh Kumar ENGG Reader 327654
11 Anuj Saxena MGT Professor 351087
Having created the Tables and having entered the data as shown in Table 8.3 and Table 8.4, the
above mentioned basic operators, viz., SELECT, PROJECT and JOIN may be used.
Example:
1. SELECT DEPTT = ‘IT’
FROM the table Teacher, we get Table 8.5 (a)
Table 8.5(a)
TCODE NAME DEPTT DESIG PHONE
06 S.C. Sharma IT Reader 219834
30 P. Gupta IT Professor 230956
2. PROJECT CNO, STDNO.
FROM the table Course, we get Table 8.5 (b).
Table 8.5(b)
CNO STDNO
CS101 25
CS201 25
CS304 25
CS406 20
CS303 20
3. Similarly, two or more than two Tables can be joined over a common field.
Example: Table course and table teacher may be joined together over a common field
TCODE to obtain the following result. (Table 8.5 (c))
Table 8.5(c)
CNO CTITLE CREDITS STDNO TCODE NAME DEPTT
CS101 MIS 6 25 07 R. Balekar MGT
CS201 SAD 4 25 15 S.C. Sharma IT
CS304 Software 4 25 30 P. Gupta IT
Engineering
CS406 Information 3 20 06 Rakesh Kumar ENGG
Technology
CS303 Strategic Systems 4 20 11 Anuj Saxena MGT
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153