Page 83 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 83
Derivatives & Risk Management
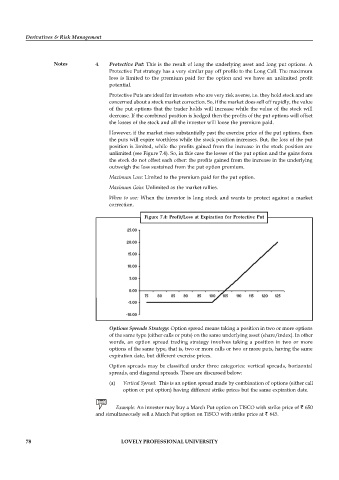
Notes 4. Protective Put: This is the result of long the underlying asset and long put options. A
Protective Put strategy has a very similar pay off profile to the Long Call. The maximum
loss is limited to the premium paid for the option and we have an unlimited profit
potential.
Protective Puts are ideal for investors who are very risk averse, i.e. they hold stock and are
concerned about a stock market correction. So, if the market does sell off rapidly, the value
of the put options that the trader holds will increase while the value of the stock will
decrease. If the combined position is hedged then the profits of the put options will offset
the losses of the stock and all the investor will loose the premium paid.
However, if the market rises substantially past the exercise price of the put options, then
the puts will expire worthless while the stock position increases. But, the loss of the put
position is limited, while the profits gained from the increase in the stock position are
unlimited (see Figure 7.4). So, in this case the losses of the put option and the gains form
the stock do not offset each other: the profits gained from the increase in the underlying
outweigh the loss sustained from the put option premium.
Maximum Loss: Limited to the premium paid for the put option.
Maximum Gain: Unlimited as the market rallies.
When to use: When the investor is long stock and wants to protect against a market
correction.
Figure 7.4: Profit/Loss at Expiration for Protective Put
Options Spreads Strategy: Option spread means taking a position in two or more options
of the same type (either calls or puts) on the same underlying asset (share/index). In other
words, an option spread trading strategy involves taking a position in two or more
options of the same type, that is, two or more calls or two or more puts, having the same
expiration date, but different exercise prices.
Option spreads may be classified under three categories: vertical spreads, horizontal
spreads, and diagonal spreads. These are discussed below:
(a) Vertical Spread: This is an option spread made by combination of options (either call
option or put option) having different strike prices but the same expiration date.
Example: An investor may buy a March Put option on TISCO with strike price of 650
and simultaneously sell a March Put option on TISCO with strike price at 645.
78 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY