Page 90 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 90
Unit 7: Option Strategies and Pay-offs
Notes
Profit/Loss on Put option
Stock Price Premium paid Net Profit /Loss
purchased
495 +45 -12 + 33
505 +35 -12 +23
515 +25 -12 +13
525 +15 -12 +3
535 +5 -12 -7
540 0 -12 -12
550 0 (NE) -12 -12
570 0 (NE) -12 -12
575 0 (NE) -12 -12
590 0 (NE) -12 -12
NE: not exercised
The maximum profit is ` 528 i.e., when the stock price takes hypothetical zero value. The
maximum loss is limited to option premium paid, i.e, ` 12.
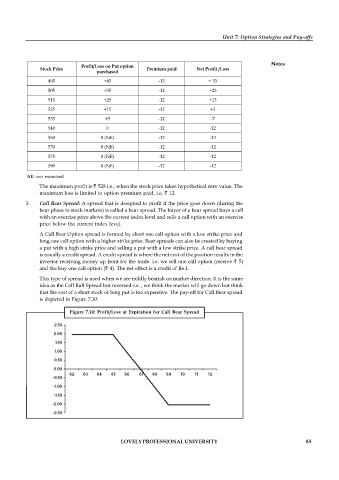
3. Call Bear Spread: A spread that is designed to profit if the price goes down (during the
bear phase in stock markets) is called a bear spread. The buyer of a bear spread buys a call
with an exercise price above the current index level and sells a call option with an exercise
price below the current index level.
A Call Bear Option spread is formed by short one call option with a low strike price and
long one call option with a higher strike price. Bear spreads can also be created by buying
a put with a high strike price and selling a put with a low strike price. A call bear spread
is usually a credit spread. A credit spread is where the net cost of the position results in the
investor receiving money up front for the trade. i.e. we sell one call option (receive ` 5)
and the buy one call option (` 4). The net effect is a credit of Re.1.
This type of spread is used when we are mildly bearish on market direction. It is the same
idea as the Call Bull Spread but reversed-i.e. , we think the market will go down but think
that the cost of a short stock or long put is too expensive. The pay-off for Call Bear spread
is depicted in Figure 7.10.
Figure 7.10: Profit/Loss at Expiration for Call Bear Spread
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 85