Page 45 - DMGT523_LOGISTICS_AND_SUPPLY_CHAIN_MANAGEMENT
P. 45
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Notes
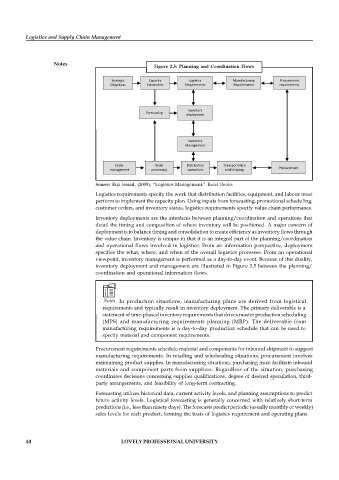
Figure 2.5: Planning and Coordination Flows
Strategic Capacity Logistics Manufacturing Procurement
Objectives Constraints Requirements Requirements requirements
Inventory
Forecasting
deployment
Inventory
Management
Order Order Distribution Transportation Procurement
management processing operations and shipping
S
Source: Reji Ismail, (2008), “Logistics Management,” Excel Books
Logistics requirements specify the work that distribution facilities, equipment, and labour must
perform to implement the capacity plan. Using inputs from forecasting, promotional scheduling,
customer orders, and inventory status, logistics requirements specify value chain performance.
Inventory deployments are the interfaces between planning/coordination and operations that
detail the timing and composition of where inventory will be positioned. A major concern of
deployment is to balance timing and consolidation to create efficiency as inventory flows through
the value chain. Inventory is unique in that it is an integral part of the planning/coordination
and operational flows involved in logistics. From an information perspective, deployment
specifies the what, where, and when of the overall logistics processes. From an operational
viewpoint, inventory management is performed as a day-to-day event. Because of this duality,
inventory deployment and management are illustrated in Figure 2.5 between the planning/
coordination and operational information flows.
Notes In production situations, manufacturing plans are derived from logistical
requirements and typically result in inventory deployment. The primary deliverable is a
statement of time-phased inventory requirements that drives master production scheduling
(MPS) and manufacturing requirements planning (MRP). The deliverable from
manufacturing requirements is a day-to-day production schedule that can be used to
specify material and component requirements.
Procurement requirements schedule material and components for inbound shipment to support
manufacturing requirements. In retailing and wholesaling situations, procurement involves
maintaining product supplies. In manufacturing situations, purchasing must facilitate inbound
materials and component parts from suppliers. Regardless of the situation, purchasing
coordinates decisions concerning supplier qualifications, degree of desired speculation, third-
party arrangements, and feasibility of long-term contracting.
Forecasting utilizes historical data, current activity levels, and planning assumptions to predict
future activity levels. Logistical forecasting is generally concerned with relatively short-term
predictions (i.e., less than ninety days). The forecasts predict periodic (usually monthly or weekly)
sales levels for each product, forming the basis of logistics requirement and operating plans.
40 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY