Page 136 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 136
Unit 8: Currency Futures and Currency Options
Stock Price Notes
At expiration, a call option must have a value that is equal to zero or the difference between the
stock price and the exercise price whichever is greater.
For example, consider that the stock price is ` 50 and the exercise price is ` 40. If the option is
selling at ` 5, an arbitrageur would make the following transactions:
Buy a call option (` 5)
Exercise the option (` 40)
Sell the stock ` 50
Net cash flow + ` 5
Hence the call price has to be greater or equal to ` 10 to prevent arbitrage opportunities.
Exercise Price
If two call options are alike, except that the exercise price of the first is less than the exercise price
of the second, then the option with the lower exercise price must have a price that is equal to or
greater than the price of the option with the higher exercise price.
For example, consider two call options on the same stock with the same time to expiration. The
first has a exercise price of ` 100 and sells for ` 10. The second has a exercise price of ` 90 and sells
for ` 5. An arbitrageur would transact as follows:
Sell the option with ` 100 exercise price +` 10
Buy the option with ` 90 exercise price (` 5)
Net cash flow ` 5
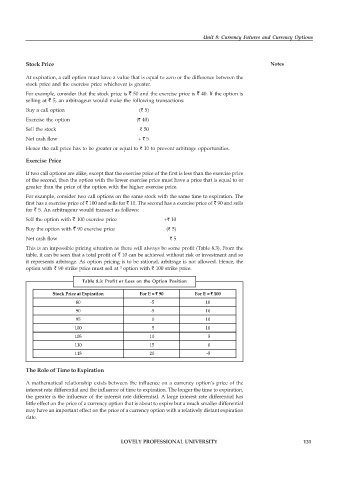
This is an impossible pricing situation as there will always be some profit (Table 8.3). From the
table, it can be seen that a total profit of ` 10 can be achieved without risk or investment and so
it represents arbitrage. As option pricing is to be rational, arbitrage is not allowed. Hence, the
option with ` 90 strike price must sell at ³ option with ` 100 strike price.
Table 8.3: Profit or Loss on the Option Position
Stock Price at Expiration For E = ` 90 For E = ` 100
80 -5 10
90 -5 10
95 0 10
100 5 10
105 10 5
110 15 0
115 20 -5
The Role of Time to Expiration
A mathematical relationship exists between the influence on a currency option’s price of the
interest rate differential and the influence of time to expiration. The longer the time to expiration,
the greater is the influence of the interest rate differential. A large interest rate differential has
little effect on the price of a currency option that is about to expire but a much smaller differential
may have an important effect on the price of a currency option with a relatively distant expiration
date.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 131