Page 84 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 84
Unit 5: Currency Forecasting
Notes
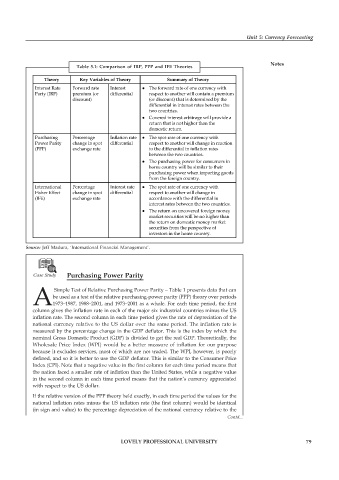
Table 5.1: Comparison of IRP, PPP and IFE Theories
Theory Key Variables of Theory Summary of Theory
Interest Rate Forward rate Interest The forward rate of one currency with
Party (IRP) premium (or differential respect to another will contain a premium
discount) (or discount) that is determined by the
differential in interest rates between the
two countries.
Covered interest arbitrage will provide a
return that is not higher than the
domestic return.
Purchasing Percentage Inflation rate The spot rate of one currency with
Power Parity change in spot differential respect to another will change in reaction
(PPP) exchange rate to the differential in inflation rates
between the two countries.
The purchasing power for consumers in
home country will be similar to their
purchasing power when importing goods
from the foreign country.
International Percentage Interest rate The spot rate of one currency with
Fisher Effect change in spot differential respect to another will change in
(IFE) exchange rate accordance with the differential in
interest rates between the two countries.
The return on uncovered foreign money
market securities will be no higher than
the return on domestic money market
securities from the perspective of
investors in the home country.
Source: Jeff Madura, ‘International Financial Management’.
Case Study Purchasing Power Parity
Simple Test of Relative Purchasing Power Parity – Table 1 presents data that can
be used as a test of the relative purchasing-power parity (PPP) theory over periods
A1973–1987, 1988–2001, and 1973–2001 as a whole. For each time period, the first
column gives the inflation rate in each of the major six industrial countries minus the US
inflation rate. The second column in each time period gives the rate of depreciation of the
national currency relative to the US dollar over the same period. The inflation rate is
measured by the percentage change in the GDP deflator. This is the index by which the
nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is divided to get the real GDP. Theoretically, the
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) would be a better measure of inflation for our purpose
because it excludes services, most of which are not traded. The WPI, however, is poorly
defined, and so it is better to use the GDP deflator. This is similar to the Consumer Price
Index (CPI). Note that a negative value in the first column for each time period means that
the nation faced a smaller rate of inflation than the United States, while a negative value
in the second column in each time period means that the nation’s currency appreciated
with respect to the US dollar.
If the relative version of the PPP theory held exactly, in each time period the values for the
national inflation rates minus the US inflation rate (the first column) would be identical
(in sign and value) to the percentage depreciation of the national currency relative to the
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 79