Page 76 - DLIS006_INFORMATION SOURCES AND SERVICES
P. 76
Unit 4: Information Services and Products
Notes
Example: Reference works are: almanac, atlas, concordance, dictionary or lexicon,
thesaurus, directory, encyclopaedia, gazetteer, and handbook, etc.
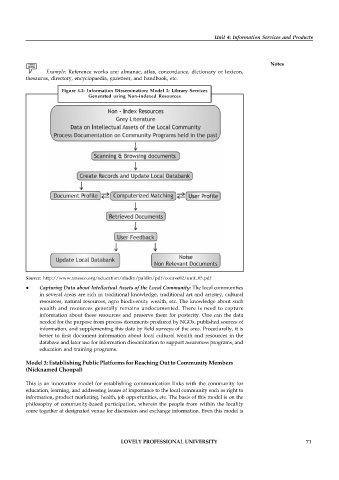
Figure 4.2: Information Dissemination: Model 2: Library Services
Generated using Non-indexed Resources
Source: http://www.unesco.org/education/aladin/paldin/pdf/course02/unit_05.pdf
Capturing Data about Intellectual Assets of the Local Community: The local communities
in several areas are rich in traditional knowledge, traditional art and artistry, cultural
resources, natural resources, agro biodiversity wealth, etc. The knowledge about such
wealth and resources generally remains undocumented. There is need to capture
information about these resources and preserve them for posterity. One can the data
needed for the purpose from process documents produced by NGOs, published sources of
information, and supplementing this data by field surveys of the area. Procedurally, it is
better to first document information about local cultural wealth and resources in the
database and later use for information dissemination to support awareness programs, and
education and training programs.
Model 3: Establishing Public Platforms for Reaching Out to Community Members
(Nicknamed Choupal)
This is an innovative model for establishing communication links with the community for
education, learning, and addressing issues of importance to the local community such as right to
information, product marketing, health, job opportunities, etc. The basis of this model is on the
philosophy of community-based participation, wherein the people from within the locality
come together at designated venue for discussion and exchange information. Even this model is
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 71