Page 75 - DLIS006_INFORMATION SOURCES AND SERVICES
P. 75
Information Sources and Services
Notes
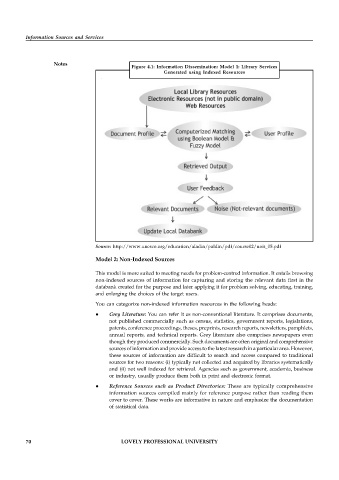
Figure 4.1: Information Dissemination: Model 1: Library Services
Generated using Indexed Resources
Source: http://www.unesco.org/education/aladin/paldin/pdf/course02/unit_05.pdf
Model 2: Non-Indexed Sources
This model is more suited to meeting needs for problem-centred information. It entails browsing
non-indexed sources of information for capturing and storing the relevant data first in the
databank created for the purpose and later applying it for problem solving, educating, training,
and enlarging the choices of the target users.
You can categorize non-indexed information resources in the following heads:
Grey Literature: You can refer it as non-conventional literature. It comprises documents,
not published commercially such as census, statistics, government reports, legislations,
patents, conference proceedings, theses, preprints, research reports, newsletters, pamphlets,
annual reports, and technical reports. Grey literature also comprises newspapers even
though they produced commercially. Such documents are often original and comprehensive
sources of information and provide access to the latest research in a particular area. However,
these sources of information are difficult to search and access compared to traditional
sources for two reasons: (i) typically not collected and acquired by libraries systematically
and (ii) not well indexed for retrieval. Agencies such as government, academia, business
or industry, usually produce them both in print and electronic format.
Reference Sources such as Product Directories: These are typically comprehensive
information sources compiled mainly for reference purpose rather than reading them
cover to cover. These works are informative in nature and emphasize the documentation
of statistical data.
70 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY