Page 122 - DLIS401_METHODOLOGY_OF_RESEARCH_AND_STATISTICAL_TECHNIQUES
P. 122
Unit 8: Measurement of Central Tendency
Notes
Did u know? For continuous variables mode provides a quick measure which is less precise
and less dependable as compared to other measures of central tendency. If
you draw a frequency polygon or a histogram, you will notice the maximum
height of this point or the bar.
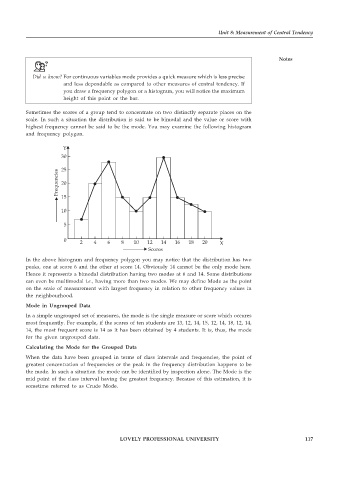
Sometimes the scores of a group tend to concentrate on two distinctly separate places on the
scale. In such a situation the distribution is said to be bimodal and the value or score with
highest frequency cannot be said to be the mode. You may examine the following histogram
and frequency polygon.
Y
30
Frequencies 25
20
15
10
5
0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 X
Scores
In the above histogram and frequency polygon you may notice that the distribution has two
peaks, one at score 6 and the other at score 14. Obviously 14 cannot be the only mode here.
Hence it represents a bimodal distribution having two modes at 6 and 14. Some distributions
can even be multimodal i.e., having more than two modes. We may define Mode as the point
on the scale of measurement with largest frequency in relation to other frequency values in
the neighbourhood.
Mode in Ungrouped Data
In a simple ungrouped set of measures, the mode is the single measure or score which occures
most frequently. For example, if the scores of ten students are 13, 12, 14, 15, 12, 14, 18, 12, 14,
14, the most frequent score is 14 as it has been obtained by 4 students. It is, thus, the mode
for the given ungrouped data.
Calculating the Mode for the Grouped Data
When the data have been grouped in terms of class intervals and frequencies, the point of
greatest concentration of frequencies or the peak in the frequency distribution happens to be
the mode. In such a situation the mode can be identified by inspection alone. The Mode is the
mid point of the class interval having the greatest frequency. Because of this estimation, it is
sometime referred to as Crude Mode.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 117