Page 232 - DCAP101_BASIC_COMPUTER_SKILLS
P. 232
Unit 11: Operations of MS Excel
7. Click the Built-In option button to display PowerPoint’s ready made custom charts. Notes
You can also add an active chart in your current presentation to the list
of chart types. Simply select the User-Defined option button on the
Custom Types tab, click the Add button, and enter details about this
active chart to the Add Custom Chart Type dialog box that appears.
Microsoft Graph adds this chart to its list of custom chart types.
8. Select the chart type you want to use from the Chart Type list. An example displays
in the Sample box.
9. Click OK to apply the chart type and return to your presentation.
11.3.5 Entering Data in the Datasheet
The default datasheet that opens when you first create a chart includes four columns
and three rows. This is a common chart format—comparing specific categories over periods
of time—but only one of the hundreds of possible formats. Figure 11.12 illustrates this
datasheet.
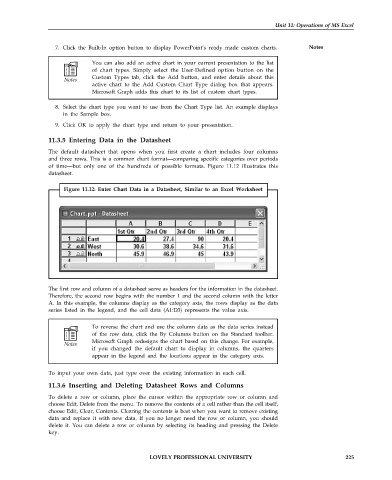
Figure 11.12: Enter Chart Data in a Datasheet, Similar to an Excel Worksheet
The first row and column of a datasheet serve as headers for the information in the datasheet.
Therefore, the second row begins with the number 1 and the second column with the letter
A. In this example, the columns display as the category axis, the rows display as the data
series listed in the legend, and the cell data (A1:D3) represents the value axis.
To reverse the chart and use the column data as the data series instead
of the row data, click the By Columns button on the Standard toolbar.
Microsoft Graph redesigns the chart based on this change. For example,
if you changed the default chart to display in columns, the quarters
appear in the legend and the locations appear in the category axis.
To input your own data, just type over the existing information in each cell.
11.3.6 Inserting and Deleting Datasheet Rows and Columns
To delete a row or column, place the cursor within the appropriate row or column and
choose Edit, Delete from the menu. To remove the contents of a cell rather than the cell itself,
choose Edit, Clear, Contents. Clearing the contents is best when you want to remove existing
data and replace it with new data. If you no longer need the row or column, you should
delete it. You can delete a row or column by selecting its heading and pressing the Delete
key.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 225