Page 95 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 95
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes Fully connected Mesh Topology
The physical fully connected mesh topology is generally too costly and complex for practical
networks, although the topology is used when there are only a small number of nodes to be
interconnected.
Partially Connected Mesh Topology
The type of network topology in which some of the nodes of the network are connected to
more than one other node in the network with a point-to-point link — this makes it possible
to take advantage of some of the redundancy that is provided by a physical fully connected
mesh topology without the expense and complexity required for a connection between every
node in the network.
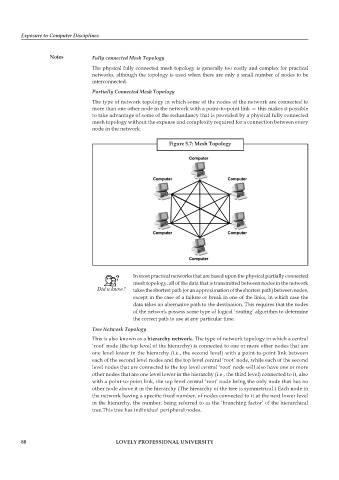
Figure 5.7: Mesh Topology
In most practical networks that are based upon the physical partially connected
mesh topology, all of the data that is transmitted between nodes in the network
takes the shortest path (or an approximation of the shortest path) between nodes,
except in the case of a failure or break in one of the links, in which case the
data takes an alternative path to the destination. This requires that the nodes
of the network possess some type of logical ‘routing’ algorithm to determine
the correct path to use at any particular time.
Tree Network Topology
This is also known as a hierarchy network. The type of network topology in which a central
‘root’ node (the top level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are
one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point link between
each of the second level nodes and the top level central ‘root’ node, while each of the second
level nodes that are connected to the top level central ‘root’ node will also have one or more
other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the third level) connected to it, also
with a point-to-point link, the top level central ‘root’ node being the only node that has no
other node above it in the hierarchy (The hierarchy of the tree is symmetrical.) Each node in
the network having a specific fixed number, of nodes connected to it at the next lower level
in the hierarchy, the number, being referred to as the ‘branching factor’ of the hierarchical
tree.This tree has individual peripheral nodes.
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY