Page 96 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 96
Unit 5: Operations of Network
(1) A network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology must have at least three Notes
levels in the hierarchy of the tree, since a network with a central ‘root’ node and only
one hierarchical level below it would exhibit the physical topology of a star.
(2) A network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology and with a branching
factor of 1 would be classified as a physical linear topology.
(3) The branching factor, f, is independent of the total number of nodes in the network and,
therefore, if the nodes in the network require ports for connection to other nodes the
total number of ports per node may be kept low even though the total number of nodes
is large — this makes the effect of the cost of adding ports to each node totally dependent
upon the branching factor and may therefore be kept as low as required without any
effect upon the total number of nodes that are possible.
(4) The total number of point-to-point links in a network that is based upon the physical
hierarchical topology will be one less than the total number of nodes in the network.
(5) If the nodes in a network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology are
required to perform any processing upon the data that is transmitted between nodes
in the network, the nodes that are at higher levels in the hierarchy will be required
to perform more processing operations on behalf of other nodes than the nodes that
are lower in the hierarchy. Such a type of network topology is very useful and highly
recommended.
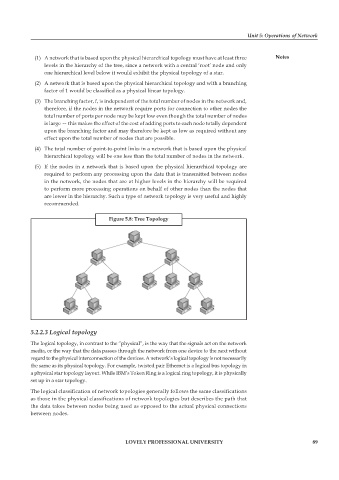
Figure 5.8: Tree Topology
5.2.2.3 Logical topology
The logical topology, in contrast to the “physical”, is the way that the signals act on the network
media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next without
regard to the physical interconnection of the devices. A network’s logical topology is not necessarily
the same as its physical topology. For example, twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in
a physical star topology layout. While IBM’s Token Ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically
set up in a star topology.
The logical classification of network topologies generally follows the same classifications
as those in the physical classifications of network topologies but describes the path that
the data takes between nodes being used as opposed to the actual physical connections
between nodes.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 89