Page 144 - DCOM102_DMGT101_PRINCIPLES_AND_PRACTICES_OF_MANAGEMENT
P. 144
Principles and Practices of Management
Notes under him is required to deal with (i) 4 direct single relationships, (ii) 12 cross relationships and
(iii) 28 group relationships, i.e., in all forty-four relationships. He derived these on the basis of
the following formula:
No. of direct relationships = n
No. of cross relationships = n [n – 1]
No. of group relationships = n [2n-1– 1]
Total No. of relationships = n [2n/2 + (n – 1) or n [2n- + n – 1]
Where n represents the number of subordinates.
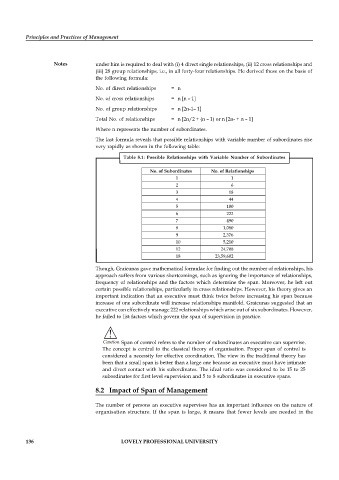
The last formula reveals that possible relationships with variable number of subordinates rise
very rapidly as shown in the following table:
Table 8.1: Possible Relationships with Variable Number of Subordinates
No. of Subordinates No. of Relationships
1 1
2 6
3 18
4 44
5 100
6 222
7 490
8 1,080
9 2,376
10 5,210
12 24,708
18 23,59,602
Though, Graicunas gave mathematical formulae for finding out the number of relationships, his
approach suffers from various shortcomings, such as ignoring the importance of relationships,
frequency of relationships and the factors which determine the span. Moreover, he left out
certain possible relationships, particularly in cross relationships. However, his theory gives an
important indication that an executive must think twice before increasing his span because
increase of one subordinate will increase relationships manifold. Graicunas suggested that an
executive can effectively manage 222 relationships which arise out of six subordinates. However,
he failed to list factors which govern the span of supervision in practice.
!
Caution Span of control refers to the number of subordinates an executive can supervise.
The concept is central to the classical theory of organisation. Proper span of control is
considered a necessity for effective coordination. The view in the traditional theory has
been that a small span is better than a large one because an executive must have intimate
and direct contact with his subordinates. The ideal ratio was considered to be 15 to 25
subordinates for first level supervision and 5 to 8 subordinates in executive spans.
8.2 Impact of Span of Management
The number of persons an executive supervises has an important influence on the nature of
organisation structure. If the span is large, it means that fewer levels are needed in the
136 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY