Page 51 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 51
Quantitative Techniques – I
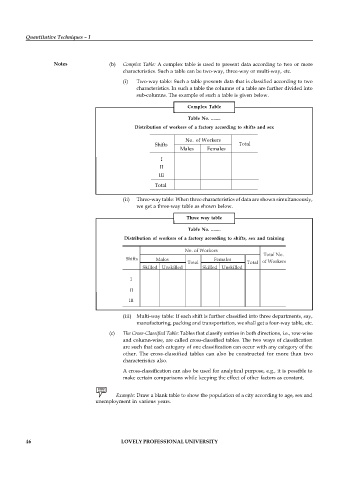
Notes (b) Complex Table: A complex table is used to present data according to two or more
characteristics. Such a table can be two-way, three-way or multi-way, etc.
(i) Two-way table: Such a table presents data that is classified according to two
characteristics. In such a table the columns of a table are further divided into
sub-columns. The example of such a table is given below.
Complex Table
Table No. ........
Distribution of workers of a factory according to shifts and sex
No. of Workers
Shifts Total
Males Females
I
II
III
Total
(ii) Three-way table: When three characteristics of data are shown simultaneously,
we get a three-way table as shown below.
Three way table
Table No. ........
Distribution of workers of a factory according to shifts, sex and training
No. of Workers
Total No.
Shifts Males Females
Total Total of Workers
Skilled Unskilled Skilled Unskilled
I
II
III
(iii) Multi-way table: If each shift is further classified into three departments, say,
manufacturing, packing and transportation, we shall get a four-way table, etc.
(c) The Cross-Classified Table: Tables that classify entries in both directions, i.e., row-wise
and column-wise, are called cross-classified tables. The two ways of classification
are such that each category of one classification can occur with any category of the
other. The cross-classified tables can also be constructed for more than two
characteristics also.
A cross-classification can also be used for analytical purpose, e.g., it is possible to
make certain comparisons while keeping the effect of other factors as constant.
Example: Draw a blank table to show the population of a city according to age, sex and
unemployment in various years.
46 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY