Page 131 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 131
Micro Economics
Notes
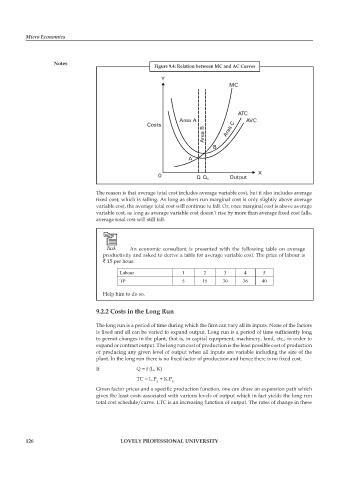
Figure 9.4: Relation between MC and AC Curves
The reason is that average total cost includes average variable cost, but it also includes average
fixed cost, which is falling. As long as short run marginal cost is only slightly above average
variable cost, the average total cost will continue to fall. Or, once marginal cost is above average
variable cost, as long as average variable cost doesn’t rise by more than average fixed cost falls,
average total cost will still fall.
Task An economic consultant is presented with the following table on average
productivity and asked to derive a table for average variable cost. The price of labour is
` 15 per hour.
Labour 1 2 3 4 5
TP 5 15 30 36 40
Help him to do so.
9.2.2 Costs in the Long Run
The long run is a period of time during which the firm can vary all its inputs. None of the factors
is fixed and all can be varied to expand output. Long run is a period of time suffi ciently long
to permit changes in the plant, that is, in capital equipment, machinery, land, etc., in order to
expand or contract output. The long run cost of production is the least possible cost of production
of producing any given level of output when all inputs are variable including the size of the
plant. In the long run there is no fixed factor of production and hence there is no fi xed cost.
If Q = f (L, K)
TC = L.P + K.P
L K
Given factor prices and a specific production function, one can draw an expansion path which
gives the least costs associated with various levels of output which in fact yields the long run
total cost schedule/curve. LTC is an increasing function of output. The rates of change in these
126 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY