Page 170 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 170
Unit 11: Monopoly
Notes
Example: In a small town there may only one general store, which has a monopoly
on the goods it sells. Because of the small size of the town, it may not be fi nancially feasible
for another company to come in – if the profits were split neither business would make
money.
6. Government monopoly: Sometimes a government will pass laws reserving a specifi c trade,
product or service for government agencies.
Example: Many times a government agency will be in charge of running water.
The legal barriers that are put up prevent other companies from competing with the
government. The entire operation is controlled either by central or state government. Their
main motive is to provide welfare to the public.
7. Simple or single monopoly: It is a type of monopoly in which a single seller controls the
entire market, by selling the commodity at a single price for all the consumers. There is no
price discrimination in the market.
8. Technological monopoly: When a firm enjoys monopoly power due to technical superiority
over other products in the market, then it is called as technological monopoly.
Example: Products produced by L & T, Godrej etc. are technological monopoly.
11.3 Price and Output Determination in Short Run
In the short run the monopolist maximises his short run profits or minimises his short run losses
if the following two conditions are satisfi ed:
1. MC = MR and
2. The slope of MC is greater than the slope of MR at the point of their intersection (i.e., MC
cuts the MR curve from below).
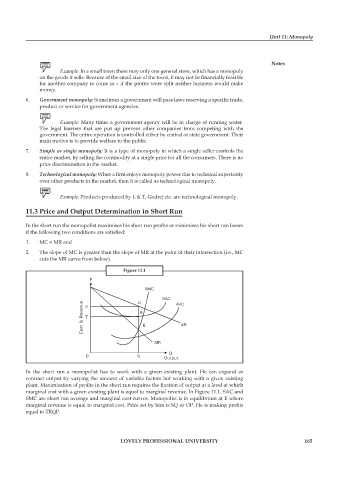
Figure 11.1
In the short run a monopolist has to work with a given existing plant. He can expand or
contract output by varying the amount of variable factors but working with a given existing
plant. Maximisation of profits in the short run requires the fixation of output at a level at which
marginal cost with a given existing plant is equal to marginal revenue. In Figure 11.1, SAC and
SMC are short run average and marginal cost curves. Monopolist is in equilibrium at E where
marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. Price set by him is SQ or OP. He is making profi ts
equal to TRQP.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 165