Page 174 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 174
Unit 11: Monopoly
Notes
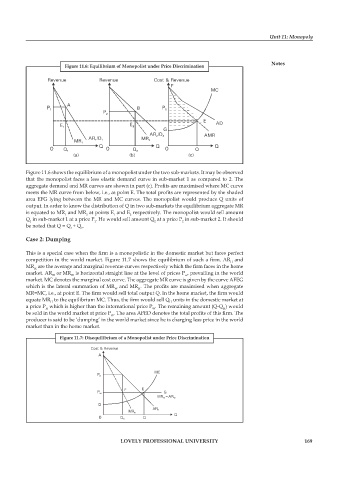
Figure 11.6: Equilibrium of Monopolist under Price Discrimination
Figure 11.6 shows the equilibrium of a monopolist under the two sub-markets. It may be observed
that the monopolist faces a less elastic demand curve in sub-market 1 as compared to 2. The
aggregate demand and MR curves are shown in part (c). Profits are maximised where MC curve
meets the MR curve from below, i.e., at point E. The total profits are represented by the shaded
area EFG lying between the MR and MC curves. The monopolist would produce Q units of
output. In order to know the distribution of Q in two sub-markets the equilibrium aggregate MR
is equated to MR and MR at points E and E respectively. The monopolist would sell amount
2
1
1
2
Q in sub-market 1 at a price P . He would sell amount Q at a price P in sub-market 2. It should
1 1 2 2
be noted that Q = Q + Q .
1
2
Case 2: Dumping
This is a special case when the firm is a monopolistic in the domestic market but faces perfect
competition in the world market. Figure 11.7 shows the equilibrium of such a fi rm. AR and
H
MR are the average and marginal revenue curves respectively which the firm faces in the home
H
market. AR or MR is horizontal straight line at the level of prices P , prevailing in the world
W
w
W
market. MC denotes the marginal cost curve. The aggregate MR curve is given by the curve AFEG
which is the lateral summation of MR and MR . The profits are maximised when aggregate
H
W
MR=MC, i.e., at point E. The firm would sell total output Q. In the home market, the fi rm would
equate MR to the equilibrium MC. Thus, the fi rm would sell Q units in the domestic market at
H
H
a price P which is higher than the international price P . The remaining amount (Q-Q ) would
H W H
be sold in the world market at price P . The area AFED denotes the total profits of this fi rm. The
W
producer is said to be ‘dumping’ in the world market since he is charging less price in the world
market than in the home market.
Figure 11.7: Disequilibrium of a Monopolist under Price Discrimination
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 169