Page 70 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 70
Unit 4: Theories of Income, Output and Employment: Keynesian Theory
4. Household's Expectation about Future: If there is a positive expectation about the future Notes
flow of income the current spending may rise. Uncertainty about future income decreases
current spending.
Consumption Function
The relation between income and consumption spending is called consumption function,
assuming all other factors influencing consumption are unchanged. It is expressed as:
C = a + bY
Where C = Consumption spending
a = Consumption spending at zero income
b = The proportion of the increased income spent on consumption
Y = Income
In the function 'a' is constant. 'b' equals change in consumption ( C) divided by the change in
income ( Y). The value of 'b' is also called Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC).
C
b = = MPC
Y
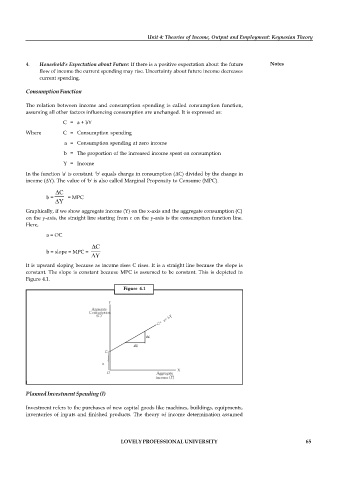
Graphically, if we show aggregate income (Y) on the x-axis and the aggregate consumption (C)
on the y-axis, the straight line starting from c on the y-axis is the consumption function line.
Here,
a = OC
C
b = slope = MPC =
Y
It is upward sloping because as income rises C rises. It is a straight line because the slope is
constant. The slope is constant because MPC is assumed to be constant. This is depicted in
Figure 4.1.
Figure 4.1
Planned Investment Spending (I)
Investment refers to the purchases of new capital goods like machines, buildings, equipments,
inventories of inputs and finished products. The theory of income determination assumed
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65