Page 74 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 74
Unit 4: Theories of Income, Output and Employment: Keynesian Theory
The approach is also called leakage/injection approach. In this approach, the equilibrium is Notes
reached when:
Planned S = Planned I
Leakages = Injections
Leakages are the outflows from the expenditure stream while injections are the fresh inflows
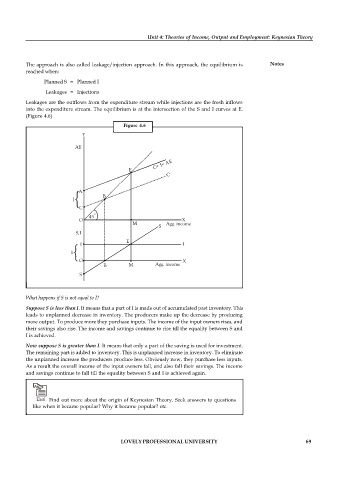
into the expenditure stream. The equilibrium is at the intersection of the S and I curves at E.
(Figure 4.6)
Figure 4.6
What happens if S is not equal to I?
Suppose S is less than I. It means that a part of I is made out of accumulated past inventory. This
leads to unplanned decrease in inventory. The producers make up the decrease by producing
more output. To produce more they purchase inputs. The income of the input owners rises, and
their savings also rise. The income and savings continue to rise till the equality between S and
I is achieved.
Now suppose S is greater than I. It means that only a part of the saving is used for investment.
The remaining part is added to inventory. This is unplanned increase in inventory. To eliminate
the unplanned increase the producers produce less. Obviously now, they purchase less inputs.
As a result the overall income of the input owners fall, and also fall their savings. The income
and savings continue to fall till the equality between S and I is achieved again.
Task Find out more about the origin of Keynesian Theory. Seek answers to questions
like when it became popular? Why it became popular? etc.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 69