Page 101 - DSOC201_SOCIAL_STRUCTURE_AND_SOCIAL_CHANGE_ENGLISH
P. 101
Social Structure and Social Change
Notes The former may further be sub-classified as large-range kinship family, inter-mediate-range kinship
family, and small-range kinship family; and the latter may be sub-classified as dependent family and
independent family.
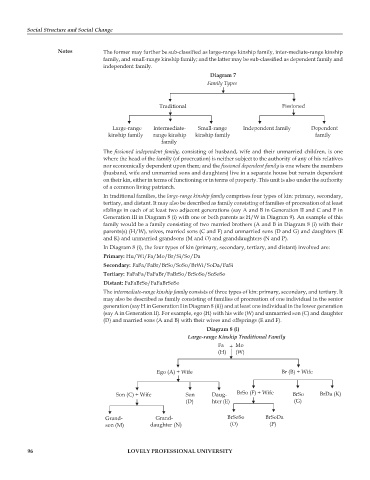
Diagram 7
Family Types
Traditional Fissioned
Large-range Intermediate- Small-range Independent family Dependent
kinship family range kinship kinship family family
family
The fissioned independent family, consisting of husband, wife and their unmarried children, is one
where the head of the family (of procreation) is neither subject to the authority of any of his relatives
nor economically dependent upon them; and the fissioned dependent family is one where the members
(husband, wife and unmarried sons and daughters) live in a separate house but remain dependent
on their kin, either in terms of functioning or in terms of property. This unit is also under the authority
of a common living patriarch.
In traditional families, the large-range kinship family comprises four types of kin: primary, secondary,
tertiary, and distant. It may also be described as family consisting of families of procreation of at least
siblings in each of at least two adjacent generations (say A and B in Generation II and C and F in
Generation III in Diagram 8 (i) with one or both parents as H/W in Diagram 9). An example of this
family would be a family consisting of two married brothers (A and B in Diagram 8 (i) with their
parents(s) (H/W), wives, married sons (C and F) and unmarried sons (D and G) and daughters (E
and K) and unmarried grandsons (M and O) and granddaughters (N and P).
In Diagram 8 (i), the four types of kin (primary, secondary, tertiary, and distant) involved are:
Primary: Hu/Wi/Fa/Mo/Br/Si/So/Da
Secondary: FaFa/FaBr/BrSo/SoSo/BrWi/SoDa/FaSi
Tertiary: FaFaFa/FaFaBr/FaBrSo/BrSoSo/SoSoSo
Distant: FaFaBrSo/FaFaBrSoSo
The intermediate-range kinship family consists of three types of kin: primary, secondary, and tertiary. It
may also be described as family consisting of families of procreation of one individual in the senior
generation (say H in Generation I in Diagram 8 (ii)) and at least one individual in the lower generation
(say A in Generation II). For example, ego (H) with his wife (W) and unmarried son (C) and daughter
(D) and married sons (A and B) with their wives and offsprings (E and F).
Diagram 8 (i)
Large-range Kinship Traditional Family
Fa + Mo
(H) (W)
Ego (A) + Wife Br (B) + Wife
Son (C) + Wife Son Daug- BrSo (F) + Wife BrSo BrDa (K)
(D) hter (E) (G)
Grand- Grand- BrSoSo BrSoDa
son (M) daughter (N) (O) (P)
96 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY