Page 102 - DSOC201_SOCIAL_STRUCTURE_AND_SOCIAL_CHANGE_ENGLISH
P. 102
Unit 4: Family
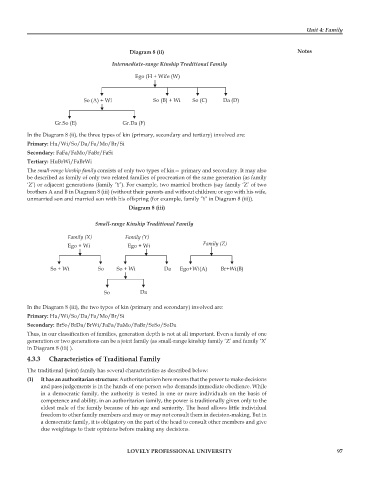
Diagram 8 (ii) Notes
Intermediate-range Kinship Traditional Family
Ego (H + Wife (W)
So (A) + Wi So (B) + Wi So (C) Da (D)
Gr.So (E) Gr.Da (F)
In the Diagram 8 (ii), the three types of kin (primary, secondary and tertiary) involved are:
Primary: Hu/Wi/So/Da/Fa/Mo/Br/Si
Secondary: FaFa/FaMo/FaBr/FaSi
Tertiary: HuBrWi/FaBrWi
The small-range kinship family consists of only two types of kin— primary and secondary. It may also
be described as family of only two related families of procreation of the same generation (as family
‘Z’) or adjacent generations (family ‘Y’). For example, two married brothers (say family ‘Z’ of two
brothers A and B in Diagram 8 (iii) (without their parents and without children; or ego with his wife,
unmarried son and married son with his offspring (for example, family ‘Y’ in Diagram 8 (iii)).
Diagram 8 (iii)
Small-range Kinship Traditional Family
Family (X) Family (Y)
Family (Z)
Ego+Wi Ego+Wi
So + Wi So So + Wi Da Ego+Wi(A) Br+Wi(B)
So Da
In the Diagram 8 (iii), the two types of kin (primary and secondary) involved are:
Primary: Hu/Wi/So/Da/Fa/Mo/Br/Si
Secondary: BrSo/BrDa/BrWi/FaFa/FaMo/FaBr/SoSo/SoDa
Thus, in our classification of families, generation depth is not at all important. Even a family of one
generation or two generations can be a joint family (as small-range kinship family ‘Z’ and family ‘X’
in Diagram 8 (iii) ).
4.3.3 Characteristics of Traditional Family
The traditional (joint) family has several characteristics as described below:
(1) It has an authoritarian structure: Authoritarianism here means that the power to make decisions
and pass judgements is in the hands of one person who demands immediate obedience. While
in a democratic family, the authority is vested in one or more individuals on the basis of
competence and ability, in an authoritarian family, the power is traditionally given only to the
eldest male of the family because of his age and seniority. The head allows little individual
freedom to other family members and may or may not consult them in decision-making. But in
a democratic family, it is obligatory on the part of the head to consult other members and give
due weightage to their opinions before making any decisions.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 97