Page 105 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 105
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes and Contract-Emps entity set to distinguish the basis on which they are paid. Then the class
hierarchy is illustrated as follows:
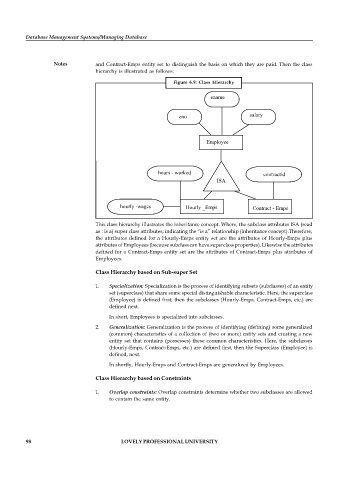
Figure 6.9: Class Hierarchy
ename
eno salary
Employee
hours - worked contractid
ISA
hourly -wages Hourly _Emps Contract - Emps
This class hierarchy illustrates the inheritance concept. Where, the subclass attributes ISA (read
as : is a) super class attributes; indicating the “is a” relationship (inheritance concept).Therefore,
the attributes defined for a Hourly-Emps entity set are the attributes of Hourly-Emps plus
attributes of Employees (because subclass can have superclass properties). Likewise the attributes
defined for a Contract-Emps entity set are the attributes of Contract-Emps plus attributes of
Employees.
Class Hierarchy based on Sub-super Set
1. Specialization: Specialization is the process of identifying subsets (subclasses) of an entity
set (superclass) that share some special distinguishable characteristic. Here, the superclass
(Employee) is defined first, then the subclasses (Hourly-Emps, Contract-Emps, etc.) are
defined next.
In short, Employees is specialized into subclasses.
2. Generalization: Generalization is the process of identifying (defining) some generalized
(common) characteristics of a collection of (two or more) entity sets and creating a new
entity set that contains (possesses) these common characteristics. Here, the subclasses
(Hourly-Emps, Contract-Emps, etc.) are defined first, then the Superclass (Employee) is
defined, next.
In shortly, Hourly-Emps and Contract-Emps are generalized by Employees.
Class Hierarchy based on Constraints
1. Overlap constraints: Overlap constraints determine whether two subclasses are allowed
to contain the same entity.
98 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY