Page 108 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 108
Unit 6: Relational Language and Database Design
Notes
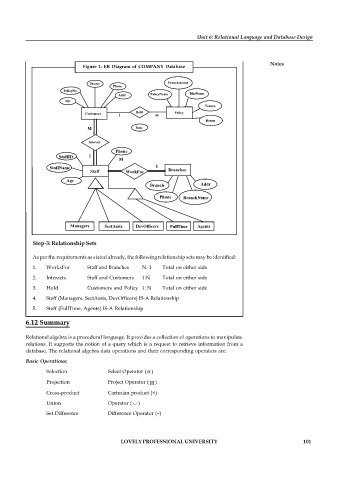
Figure 1: ER Diagram of COMPANY Database
IName PremAmount
Phone
PolicyNo
Addr PolicyName MatName
Age
Tenure
Customers 1 Hold M Policy
Bonus
M Date
Interact
Phone
StaffID 1
M
StaffName 1 Branches
Staff WorkFor
Age
Branch Addr
Phone BranchName
Managers SectAssts DevOfficers FullTime Agents
Step-3: Relationship Sets
As per the requirements as stated already, the following relationship sets may be identified:
1. WorksFor Staff and Branches N: 1 Total on either side
2. Interacts Staff and Customers 1:N Total on either side
3. Hold Customers and Policy 1: N Total on either side
4. Staff (Managers, SectAssts, DevOfficers) IS-A Relationship
5. Staff (FullTime, Agents) IS-A Relationship
6.12 Summary
Relational algebra is a procedural language. It provides a collection of operations to manipulate
relations. It supports the notion of a query which is a request to retrieve information from a
database. The relational algebra data operations and their corresponding operators are:
Basic Operations:
Selection Select Operator ( )
Projection Project Operator ( )
Cross-product Cartesian product (×)
Union Operator ( )
Set Difference Difference Operator (–)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 101