Page 166 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 166
Unit 9: Transaction Management
The validation test for transaction T requires that, for all transactions T with TS(T ) < TS(T), one Notes
j i i j
of the following two conditions must hold:
1. Finish(T ) < Start(T) Since T completes its execution before T started, the serializability
i j i j
order is indeed maintained.
2. The set of data items written by T does not intersect with the set of data items read by T,
i
and T completes its write phase before T starts its validation phase (Start(T) < Finish(T ) <
i j j i
Validation(T )). This condition ensures that the writes of T and T do not overlap. Since the
j i j
writes of T do not affect the read of T , and since T cannot affect the read of T the
i j j i
serializability order is indeed maintained.
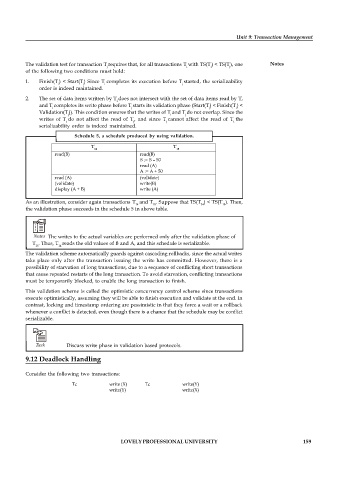
Schedule 5, a schedule produced by using validation.
T T
14 15
read(B) read(B)
B := B – 50
read (A)
A := A + 50
read (A) (validate)
(validate) write(B)
display (A + B) write (A)
As an illustration, consider again transactions T and T . Suppose that TS(T ) < TS(T ). Then,
14 15 14 15
the validation phase succeeds in the schedule 5 in above table.
Notes The writes to the actual variables are performed only after the validation phase of
T . Thus, T reads the old values of B and A, and this schedule is serializable.
15 14
The validation scheme automatically guards against cascading rollbacks, since the actual writes
take place only after the transaction issuing the write has committed. However, there is a
possibility of starvation of long transactions, due to a sequence of conflicting short transactions
that cause repeated restarts of the long transaction. To avoid starvation, conflicting transactions
must be temporarily blocked, to enable the long transaction to finish.
This validation scheme is called the optimistic concurrency control scheme since transactions
execute optimistically, assuming they will be able to finish execution and validate at the end. In
contrast, locking and timestamp ordering are pessimistic in that they force a wait or a rollback
whenever a conflict is detected, even though there is a chance that the schedule may be conflict
serializable.
Task Discuss write phase in validation based protocols.
9.12 Deadlock Handling
Consider the following two transactions:
T1: write (X) T2: write(Y)
write(Y) write(X)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 159