Page 199 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 199
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes
Case Study Remote Backup Systems
R emote backup systems provide high availability by allowing transaction processing
to continue even if the primary site is destroyed.
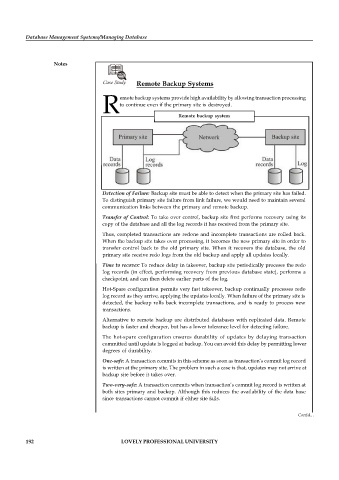
Remote backup system
Detection of Failure: Backup site must be able to detect when the primary site has failed.
To distinguish primary site failure from link failure, we would need to maintain several
communication links between the primary and remote backup.
Transfer of Control: To take over control, backup site first performs recovery using its
copy of the database and all the log records it has received from the primary site.
Thus, completed transactions are redone and incomplete transactions are rolled back.
When the backup site takes over processing, it becomes the new primary site in order to
transfer control back to the old primary site. When it recovers the database, the old
primary site receive redo logs from the old backup and apply all updates locally.
Time to recover: To reduce delay in takeover, backup site periodically proceses the redo
log records (in effect, performing recovery from previous database state), performs a
checkpoint, and can then delete earlier parts of the log.
Hot-Spare configuration permits very fast takeover, backup continually processes redo
log record as they arrive, applying the updates locally. When failure of the primary site is
detected, the backup rolls back incomplete transactions, and is ready to process new
transactions.
Alternative to remote backup are distributed databases with replicated data. Remote
backup is faster and cheaper, but has a lower tolerance level for detecting failure.
The hot-spare configuration ensures durability of updates by delaying transaction
committed until update is logged at backup. You can avoid this delay by permitting lower
degrees of durability.
One-safe: A transaction commits in this scheme as soon as transaction’s commit log record
is written at the primary site. The problem in such a case is that, updates may not arrive at
backup site before it takes over.
Two-very-safe: A transaction commits when transaction’s commit log record is written at
both sites primary and backup. Although this reduces the availability of the data base
since transactions cannot commit if either site fails.
Contd...
192 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY