Page 183 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 183
Microeconomic Theory
Notes has not to pay rent to anyone . But on giving, this building on rent to another person the rent which it
can get from that building, it has to sacrifice this loss. In economics, a firm's own resources opportunity
cost is called implicit costs.
According to Leftwitch, “Implicit costs are costs of self-owned and self-employed resources.”
—Leftwitch
For a firm implicit costs are those monetary payments which the firm for better uses of its own resources
can get by selling or giving on rent. Like explicit costs, implicit costs are also the sacrifices done by the firm.
But in contrast to explicit costs these are not paid to other people. The implicit cost is equal to that
Imputed Value of self owner and self consuming products which can get by superior optional product.
For an economist, the cost of a factor is equal to its price which a firm expends on the factor for not on its
own but for another firm. For example, Ram is a sole proprietor of a book shop. The building is his own.
He puts the cost in his industry and work alone. Means however he does not need to pay anything like
wages or rent to run his business means there is no Explicit Cost with him. But he needs to bear Implicit
Costs like wages, interest etc. He can earn 400 by renting his building for a shop to anyone. Thus by
using his own building, he is scarifying for 400. Thus, he is scarifying the interest which he could get
form his capital. If Ram is not running his shop, he could work on another shop and earn wages. But
to run his firm, he is scarifying from this amount too. The Normal Profit is the minimum income which
Ram needs to run his firm. Normal Profit is the implicit cost of Ram’s firm. This is also included in total
cost. Thus the implicit cost and actual cost are included in Total cost.
9.2 Costs in the Short Run
Since short-term productivity costs close relationship, so a short-term productivity cost is related to
each measurement. Which means like stable and variable resources, fixed and variable costs are exist.
Similarly, the way on which total, average and aggregates of production are measured in the same
total, average and aggregates of costs are measured. In short, cost and productivity are mutual.
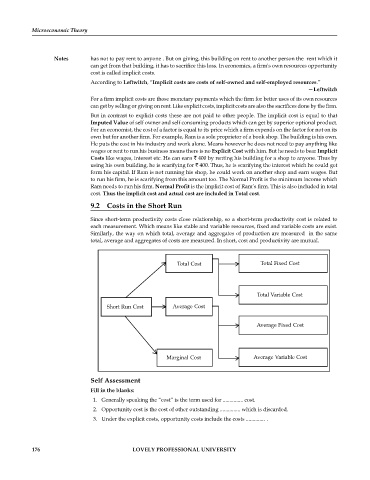
Total Cost Total Fixed Cost
Total Variable Cost
Short Run Cost Average Cost
Average Fixed Cost
Marginal Cost Average Variable Cost
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Generally speaking the “cost” is the term used for ............... cost.
2. Opportunity cost is the cost of other outstanding ............... which is discarded.
3. Under the explicit costs, opportunity costs include the costs .............. .
176 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY