Page 184 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 184
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
9.3 Total Cost Notes
To produce different levels of an object, the money which has to spend is called the total cost. In short
term fixed and variable modes are divided into two categories, similarly, the firm’s total production
costs are divided into two categories. Total fixed costs and variable costs of fixed assets to total variable
costs is the cost of resources. Thus, total cost is the sum of total fixed cost and variable cost.
TC = TFC + TVC
(Here, TC = Total Cost, TFC = Total Fix Costs, TVC = Total Variable Costs)
In the words of Browning, “Total cost (TC) is the sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost for
each output level.” The total cost required for the production of an object by means of the cost of all
fixed and variable resources appear. The total cost is always increasing with output. The cause of this is
that for increasing production always require more resources.
Total Fixed or Supplementary Costs
In short term, the cost of fixed assets is called total fixed costs. Fixed costs are the product of the units
and the prices of fixed asset .
Total Fixed Cost (TFC) = Units of Fixed Resource × Price of Fixed Cost
These costs do not change with the volume of production. If the output is zero, the cost will remain
stable.
In the words of Ferguson, “Total fixed cost is the sum of the short run explicit fixed costs and the
implicit costs incurred by an entrepreneur.”
—Ferguson
Some fixed costs do not change with the volume of production. If a firm stops production for sometime
even it has to pay the total fixed cost.
In a carpet rug factory more and more carpets can be made in a day. The manufacturing fixed cost of
carpet is ` 100. In that factory even a single piece of carpet is not made in a day, fixed cost will remain
` 100. If on the second day six carpets are made then also fixed cost will remain ` 100. This is also
called supplementary cost on indirect cost or overhead cost on Historical costs or unavoidable costs.
In fixed cost following expenditures are included. – (1) Rent (2) Depreciation (3) Manager, salaries
of administration (4) Interest on fixed capital (5) Lessons fees (6) general benefit and (7) depreciation
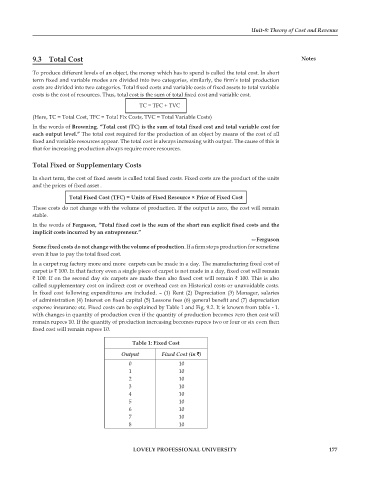
expense insurance etc. Fixed costs can be explained by Table 1 and Fig. 9.2. It is known from table - 1.
with changes in quantity of production even if the quantity of production becomes zero then cost will
remain rupees 10. If the quantity of production increasing becomes rupees two or four or six even then
fixed cost will remain rupees 10.
Table 1: Fixed Cost
Output Fixed Cost (in )
0 10
1 10
2 10
3 10
4 10
5 10
6 10
7 10
8 10
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177