Page 189 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 189
Microeconomic Theory
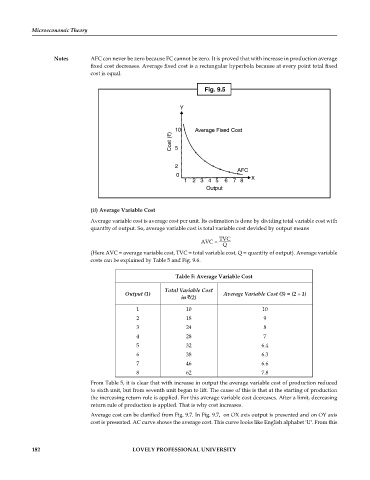
Notes AFC can never be zero because FC cannot be zero. It is proved that with increase in production average
fixed cost decreases. Average fixed cost is a rectangular hyperbola because at every point total fixed
cost is equal.
Fig. 9.5
Y
10 Average Fixed Cost
Cost (`) 5
2
AFC
0
12 3 45 6 7 8 X
Output
(ii) Average Variable Cost
Average variable cost is average cost per unit. Its estimation is done by dividing total variable cost with
quantity of output. So, average variable cost is total variable cost devided by output means
TVC
AVC = _____
Q
(Here AVC = average variable cost, TVC = total variable cost, Q = quantity of output). Average variable
costs can be explained by Table 5 and Fig. 9.6.
Table 5: Average Variable Cost
Total Variable Cost
Output (1) Average Variable Cost (3) = (2 ÷ 1)
in (2)
1 10 10
2 18 9
3 24 8
4 28 7
5 32 6.4
6 38 6.3
7 46 6.6
8 62 7.8
From Table 5, it is clear that with increase in output the average variable cost of production reduced
to sixth unit, but from seventh unit began to lift. The cause of this is that at the starting of production
the increasing return rule is applied. For this average variable cost decreases. After a limit, decreasing
return rule of production is applied. That is why cost increases.
Average cost can be clarified from Fig. 9.7. In Fig. 9.7, on OX axis output is presented and on OY axis
cost is presented. AC curve shows the average cost. This curve looks like English alphabet 'U'. From this
182 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY