Page 190 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 190
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
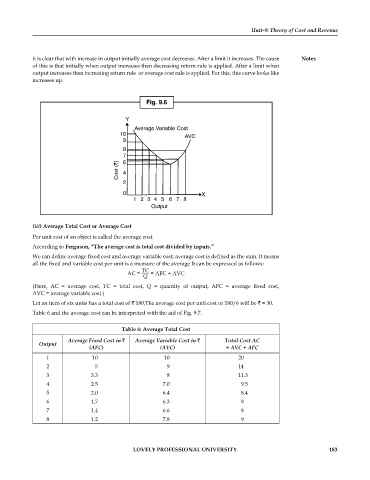
it is clear that with increase in output initially average cost decreases. After a limit it increases. The cause Notes
of this is that initially when output increases then decreasing return rule is applied. After a limit when
output increases then increasing return rule or average cost rule is applied. For this, this curve looks like
increases up.
Fig. 9.6
Y
Average Variable Cost
10 AVC
9
8
7
6
Cost (`) 4
2
0 X
12 3 45 6 7 8
Output
(iii) Average Total Cost or Average Cost
Per unit cost of an object is called the average cost.
According to Ferguson, “The average cost is total cost divided by inputs.”
We can define average fixed cost and average variable cost; average cost is defined as the sum. It means
all the fixed and variable cost per unit is a measure of the average It can be expressed as follows:
TC
___
AC = = AFC + AVC
Q
(Here, AC = average cost, TC = total cost, Q = quantity of output, AFC = average fixed cost,
AVC = average variable cost.)
Let an item of six units has a total cost of 180,The average cost per unit cost or 180/6 will be = 30.
Table 6 and the average cost can be interpreted with the aid of Fig. 9.7.
Table 6: Average Total Cost
Average Fixed Cost in Average Variable Cost in Total Cost AC
Output
(AFC) (AVC) = AVC + AFC
1 10 10 20
2 5 9 14
3 3.3 8 11.3
4 2.5 7.0 9.5
5 2.0 6.4 8.4
6 1.7 6.3 8
7 1.4 6.6 8
8 1.2 7.8 9
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 183