Page 195 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 195
Microeconomic Theory
Notes 2. When AC rises, MC is greater than AC: If the average cost increases marginal cost also increases, but
the marginal cost rises faster than the average cost. This is because of the Law of Diminishing Returns.
Average Cost (AC) in the Fixed Cost (FC) reduces the rate of increase in the fraction. Marginal and
average cost curves up the slope and then the MC curve is above the curve AC.
3. MC Cuts AC at its Lowest Point: The lowest average cost will be equal to the marginal cost. In
other words, the marginal cost curve is U-shaped average cost curve at its lowest point. Table 8 is
determined by the lowest average cost that is the seventh unit is 8. Seventh unit's marginal cost
(MC) is the 8 rupees. Figure 9.9 is determined by the marginal cost curve (MC), Average Cost (AC)
curve at the minimum point E is cut. This should take care of the marginal cost curve the average
cost of the lowest point of the average cost has come before. Table 8 is determined by the marginal
cost (MC) is the lowest point on the fifth unit, while the average cost at the lowest point is the seventh
unit. The question is why is it produced? There is no economic reason. Marginal and average curve
is characterized primarily mathematical.
When AC is stable then AC = MC. In contrast, when the AC is falling AC > MC, but when the AC is
increasing MC > AC.
9.10 Relationship of Different Cost Curves in the Short Period
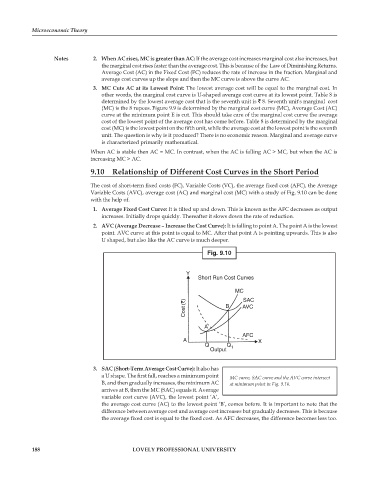
The cost of short-term fixed costs (FC), Variable Costs (VC), the average fixed cost (AFC), the Average
Variable Costs (AVC), average cost (AC) and marginal cost (MC) with a study of Fig. 9.10 can be done
with the help of.
1. Average Fixed Cost Curve: It is tilted up and down. This is known as the AFC decreases as output
increases. Initially drops quickly. Thereafter it slows down the rate of reduction.
2. AVC (Average Decrease – Increase the Cost Curve): It is falling to point A. The point A is the lowest
point. AVC curve at this point is equal to MC. After that point A is pointing upwards. This is also
U shaped, but also like the AC curve is much deeper.
Fig. 9.10
Y
Short Run Cost Curves
MC
SAC
Cost (`) B AVC
A
AFC
A X
Q Q 1
Output
3. SAC (Short-Term Average Cost Curve): It also has
a U shape. The first fall, reaches a minimum point MC curve, SAC curve and the AVC curve intersect
B, and then gradually increases, the minimum AC at minimum point in Fig. 9.10.
arrives at B, then the MC (SAC) equals it. Average
variable cost curve (AVC), the lowest point ‘A’,
the average cost curve (AC) to the lowest point ‘B’, comes before. It is important to note that the
difference between average cost and average cost increases but gradually decreases. This is because
the average fixed cost is equal to the fixed cost. As AFC decreases, the difference becomes less too.
188 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY