Page 198 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 198
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
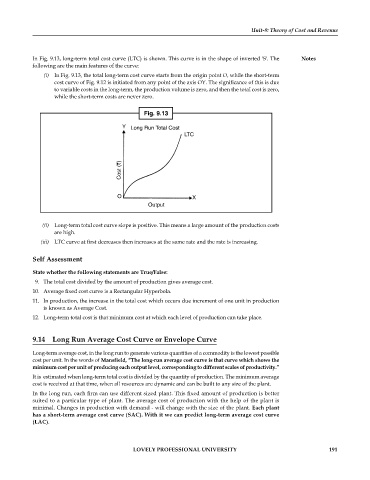
In Fig. 9.13, long-term total cost curve (LTC) is shown. This curve is in the shape of inverted 'S'. The Notes
following are the main features of the curve:
(i) In Fig. 9.13, the total long-term cost curve starts from the origin point O, while the short-term
cost curve of Fig. 9.12 is initiated from any point of the axis OY. The significance of this is due
to variable costs in the long-term, the production volume is zero, and then the total cost is zero,
while the short-term costs are never zero.
Fig. 9.13
Y Long Run Total Cost
LTC
Cost (`)
O X
Output
(ii) Long-term total cost curve slope is positive. This means a large amount of the production costs
are high.
(iii) LTC curve at first decreases then increases at the same rate and the rate is increasing.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are True/False:
9. The total cost divided by the amount of production gives average cost.
10. Average fixed cost curve is a Rectangular Hyperbola.
11. In production, the increase in the total cost which occurs due increment of one unit in production
is known as Average Cost.
12. Long-term total cost is that minimum cost at which each level of production can take place.
9.14 Long Run Average Cost Curve or Envelope Curve
Long-term average cost, in the long run to generate various quantities of a commodity is the lowest possible
cost per unit. In the words of Mansfield, “The long-run average cost curve is that curve which shows the
minimum cost per unit of producing each output level, corresponding to different scales of productivity.”
It is estimated when long-term total cost is divided by the quantity of production. The minimum average
cost is received at that time, when all resources are dynamic and can be built to any size of the plant.
In the long run, each firm can use different sized plant. This fixed amount of production is better
suited to a particular type of plant. The average cost of production with the help of the plant is
minimal. Changes in production with demand - will change with the size of the plant. Each plant
has a short-term average cost curve (SAC). With it we can predict long-term average cost curve
(LAC).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 191