Page 200 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 200
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
Notes
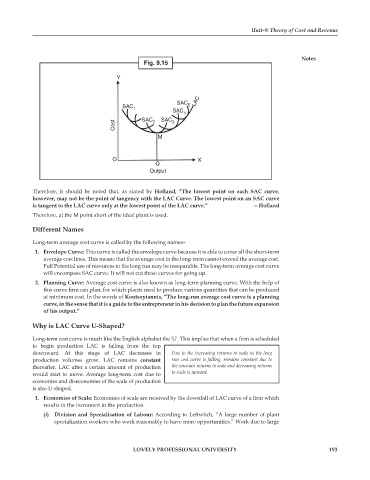
Fig. 9.15
Y
SAC 5 LAC
SAC
1
SAC
4
Cost SAC 2 SAC 3
M
O X
Q
Output
Therefore, it should be noted that, as stated by Holland, “The lowest point on each SAC curve,
however, may not be the point of tangency with the LAC Curve. The lowest point on an SAC curve
is tangent to the LAC curve only at the lowest point of the LAC curve.” —Holland
Therefore, at the M point short of the ideal plant is used.
Different Names
Long-term average cost curve is called by the following names–
1. Envelope Curve: This curve is called the envelope curve because it is able to cover all the short-term
average cost lines. This means that the average cost in the long-term cannot exceed the average cost.
Full Potential use of resources in the long run may be inseparable. The long-term average cost curve
will encompass SAC curve. It will not cut these curves for going up.
2. Planning Curve: Average cost curve is also known as long-term planning curve. With the help of
this curve firm can plan, for which plants used to produce various quantities that can be produced
at minimum cost. In the words of Koutsoyiannis, “The long-run average cost curve is a planning
curve, in the sense that it is a guide to the entrepreneur in his decision to plan the future expansion
of his output.”
Why is LAC Curve U-Shaped?
Long-term cost curve is much like the English alphabet the 'U'. This implies that when a firm is scheduled
to begin production LAC is falling from the top
downward. At this stage of LAC decreases in Due to the increasing returns to scale in the long
production volumes grow. LAC remains constant run cost curve is falling, remains constant due to
thereafter. LAC after a certain amount of production the constant returns to scale and decreasing returns
would start to move. Average long-term cost due to to scale is upward.
economies and diseconomies of the scale of production
is also U-shaped.
1. Economies of Scale: Economies of scale are received by the downfall of LAC curve of a firm which
results in the increment in the production.
(i) Division and Specialisation of Labour: According to Leftwitch, “A large number of plant
specialization workers who work reasonably to have more opportunities.” Work due to large
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 193