Page 202 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 202
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
(i) Relation between Long Run and Short Run Marginal Cost: The marginal cost curve determines Notes
a short, decreasing - increasing changes in the volume of an object to produce a more or less
consequent impact on total cost. In contrast, it is determined by long-term cost curve, changes
in the modes of production of a commodity, to a greater or lesser amount, consequent impact
on the total cost.
In the long run we all know that all instruments are subject to change. Short-term marginal
cost curve is determined by the marginal cost curve, but it does not envelops them. Long-term
marginal cost of production and short-term marginal cost (SMC) at that level (LMC), must be
equal. SMC regarding the long-term average real cost curve (LAC) is a tangent.
When a firm develops an appropriate scale of the plant for the production of the object then,
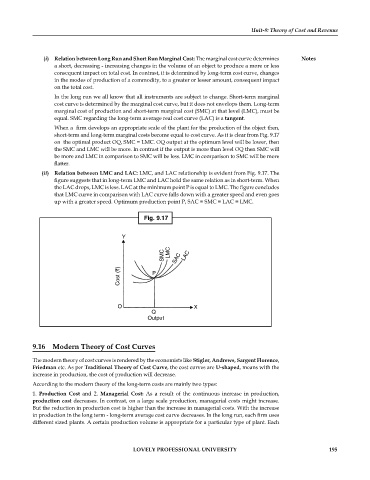
short-term and long-term marginal costs become equal to cost curve. As it is clear from Fig. 9.17
on the optimal product OQ, SMC = LMC. OQ output at the optimum level will be lower, then
the SMC and LMC will be more. In contrast if the output is more than level OQ then SMC will
be more and LMC in comparison to SMC will be less. LMC in comparison to SMC will be more
flatter.
(ii) Relation between LMC and LAC: LMC, and LAC relationship is evident from Fig. 9.17. The
figure suggests that in long-term LMC and LAC hold the same relation as in short-term. When
the LAC drops, LMC is less. LAC at the minimum point P is equal to LMC. The figure concludes
that LMC curve in comparison with LAC curve falls down with a greater speed and even goes
up with a greater speed. Optimum production point P, SAC = SMC = LAC = LMC.
Fig. 9.17
Y
SMC LMC SAC LAC
Cost (`) P
O X
Q
Output
9.16 Modern Theory of Cost Curves
The modern theory of cost curves is rendered by the economists like Stigler, Andrews, Sargent Florence,
Friedman etc. As per Traditional Theory of Cost Curve, the cost curves are U-shaped, means with the
increase in production, the cost of production will decrease.
According to the modern theory of the long-term costs are mainly two types:
1. Production Cost and 2. Managerial Cost: As a result of the continuous increase in production,
production cost decreases. In contrast, on a large scale production, managerial costs might increase.
But the reduction in production cost is higher than the increase in managerial costs. With the increase
in production in the long term - long-term average cost curve decreases. In the long run, each firm uses
different sized plants. A certain production volume is appropriate for a particular type of plant. Each
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 195